Page 134 - DCAP201_FUNDAMENTALS_OF_DATA_STRUCTURES
P. 134
Unit 8: Operations on Linked List
newNode—>next = newNode; Notes
if(*head ==NULL)
*head = newNode;
else { newNode—>next = *head;
current—>next = newNode;
*head = newNode;
}
Return;
}
8.3.4 Circular Linked List Deletion
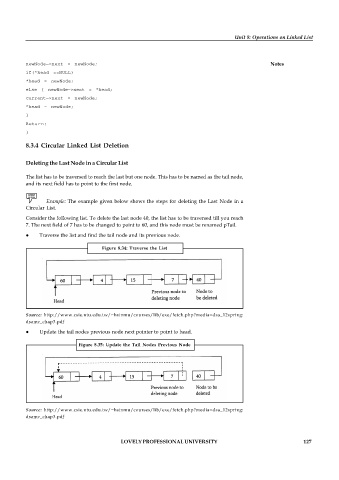
Deleting the Last Node in a Circular List
The list has to be traversed to reach the last but one node. This has to be named as the tail node,
and its next field has to point to the first node.
Example: The example given below shows the steps for deleting the Last Node in a
Circular List.
Consider the following list. To delete the last node 40, the list has to be traversed till you reach
7. The next field of 7 has to be changed to point to 60, and this node must be renamed pTail.
Traverse the list and find the tail node and its previous node.
Figure 8.34: Traverse the List
Source: http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~hsinmu/courses/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=dsa_12spring:
dsame_chap3.pdf
Update the tail nodes previous node next pointer to point to head.
Figure 8.35: Update the Tail Nodes Previous Node
Source: http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~hsinmu/courses/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=dsa_12spring:
dsame_chap3.pdf
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 127