Page 208 - DCAP201_FUNDAMENTALS_OF_DATA_STRUCTURES
P. 208
Unit 12: Introduction to Trees
This is the recursive algorithm for INORDER traversal. Notes
C implementation is given as below.
struct NODE
{
struct NODE *left;
int value;
struct NODE *right;
}
inorder(struct NODE *curr)
{
if(curr->left != NULL) inorder(curr->left); /*step-1 & step-2*/
printf(“%d”, curr->value); /*step-3*/
if(curr->right != NULL) inorder(curr->right); /*step-4*/
}
Task Make distinction between pre-order and post-order.
12.3.1 Threaded Binary Tree
Trees->Threaded Binary Tree->Concepts
A Threaded Binary Tree is a binary tree in which every node that does not have a right child has
a THREAD (in actual sense, a link) to its INORDER successor. By doing this threading we avoid
the recursive method of traversing a Tree, which makes use of stacks and consumes a lot of
memory and time.
The node structure for a threaded binary tree varies a bit and its like this:
struct NODE
{
struct NODE *leftchild;
int node_value;
struct NODE *rightchild;
struct NODE *thread;
}
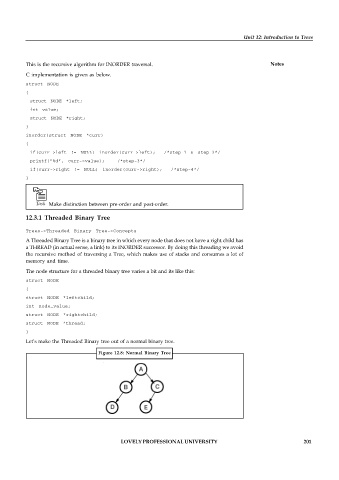
Let’s make the Threaded Binary tree out of a normal binary tree.
Figure 12.8: Normal Binary Tree
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 201