Page 236 - DCAP201_FUNDAMENTALS_OF_DATA_STRUCTURES
P. 236
Unit 13: Sorting
Dynamic Hashing Notes
Since static hashing had a problem of bucket overflow and slow processing was an added
disadvantage dynamic hashing was introduced. It is more effective than static hashing where
the database can grow and sink.
Extendable hashing allows dynamic allocation of buckets, i.e. according to the demand of database
the buckets can be allocated making this approach more efficient. The hash function produces a
large number of values but only a part of the value is used to map. Hash indices are used from
an indexed table which is used as prefix of an entire hash value. More than one consecutive index
can point to a specific bucket.
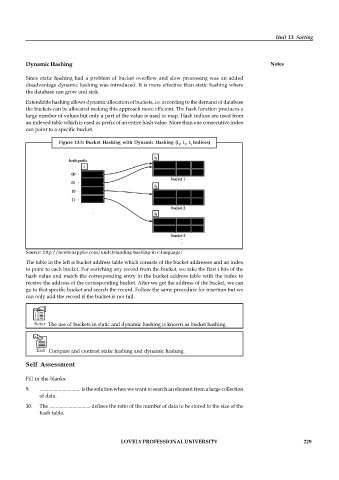
Figure 13.5: Bucket Hashing with Dynamic Hashing (i , i , i Indices)
1 2 3
Source: http://newtonapples.com/understanding-hashing-in-c-language/
The table in the left is bucket address table which consists of the bucket addresses and an index
to point to each bucket. For searching any record from the bucket, we take the first i bits of the
hash value and match the corresponding entry in the bucket address table with the index to
receive the address of the corresponding bucket. After we get the address of the bucket, we can
go to that specific bucket and search the record. Follow the same procedure for insertion but we
can only add the record if the bucket is not full.
Notes The use of buckets in static and dynamic hashing is known as bucket hashing.
Task Compare and contrast static hashing and dynamic hashing.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
9. ................................ is the solution when we want to search an element from a large collection
of data.
10. The ................................ defines the ratio of the number of data to be stored to the size of the
hash table.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 229