Page 81 - DCAP202_Fundamentals of Web Programming
P. 81
Fundamentals of Web Programming
Notes var b5 = Boolean(0); //false - zero
var b6 = Boolean(new Object()); //true – object
The Number() type cast works in a manner similar to parseInt() and parseFloat() , except that it
converts the entire value, not just part of it. Remember that parseInt() and parseFloat() only
convert up to the first invalid character (in strings), so “4.5.6” becomes “4.5” . Using the Number()
type cast, “4.5.6” becomes NaN because the entire string value cannot be converted into a
number. If a string value can be converted entirely, Number() decides whether to use parseInt()
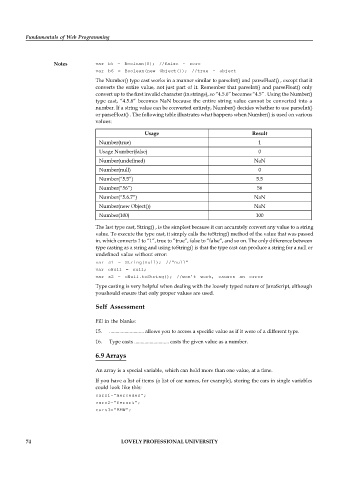
or parseFloat() . The following table illustrates what happens when Number() is used on various
values:
Usage Result
Number(true) 1
Usage Number(false) 0
Number(undefined) NaN
Number(null) 0
Number(“5.5”) 5.5
Number(“56”) 56
Number(“5.6.7”) NaN
Number(new Object()) NaN
Number(100) 100
The last type cast, String() , is the simplest because it can accurately convert any value to a string
value. To execute the type cast, it simply calls the toString() method of the value that was passed
in, which converts 1 to “1”, true to “true”, false to “false”, and so on. The only difference between
type casting as a string and using toString() is that the type cast can produce a string for a null or
undefined value without error:
var s1 = String(null); //”null”
var oNull = null;
var s2 = oNull.toString(); //won’t work, causes an error
Type casting is very helpful when dealing with the loosely typed nature of JavaScript, although
youshould ensure that only proper values are used.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
15. ........................... allows you to access a specific value as if it were of a different type.
16. Type casts ........................... casts the given value as a number.
6.9 Arrays
An array is a special variable, which can hold more than one value, at a time.
If you have a list of items (a list of car names, for example), storing the cars in single variables
could look like this:
cars1=”mercedes”;
cars2=”ferari”;
cars3=”BMW”;
74 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY