Page 87 - DCAP202_Fundamentals of Web Programming
P. 87
Fundamentals of Web Programming
Notes
Example: One variable is a higher number than the other. Other operators perform an
action on a variable, such as increasing it by one.
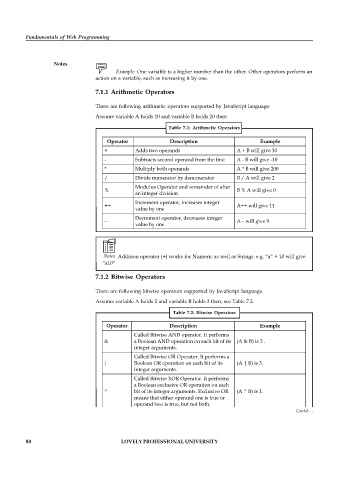
7.1.1 Arithmetic Operators
There are following arithmetic operators supported by JavaScript language:
Assume variable A holds 10 and variable B holds 20 then:
Table 7.1: Arithmetic Operators
Operator Description Example
+ Adds two operands A + B will give 30
- Subtracts second operand from the first A - B will give -10
* Multiply both operands A * B will give 200
/ Divide numerator by denumerator B / A will give 2
Modulus Operator and remainder of after
% B % A will give 0
an integer division
Increment operator, increases integer
++ A++ will give 11
value by one
Decrement operator, decreases integer
-- A-- will give 9
value by one
Notes Addition operator (+) works for Numeric as well as Strings. e.g. “a” + 10 will give
“a10”
7.1.2 Bitwise Operators
There are following bitwise operators supported by JavaScript language.
Assume variable A holds 2 and variable B holds 3 then, see Table 7.2.
Table 7.2: Bitwise Operators
Operator Description Example
Called Bitwise AND operator. It performs
& a Boolean AND operation on each bit of its (A & B) is 2 .
integer arguments.
Called Bitwise OR Operator. It performs a
| Boolean OR operation on each bit of its (A | B) is 3.
integer arguments.
Called Bitwise XOR Operator. It performs
a Boolean exclusive OR operation on each
^ bit of its integer arguments. Exclusive OR (A ^ B) is 1.
means that either operand one is true or
operand two is true, but not both.
Contd....
Called Bitwise NOT Operator. It is a is a
~ unary operator and operates by reversing (~B) is -4 .
all bits in the operand.
Called Bitwise Shift Left Operator. It
moves all bits in its first operand to the left
80 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY
by the number of places specified in the
second operand. New bits are filled with
<< (A << 1) is 4.
zeros. Shifting a value left by one position
is equivalent to multiplying by 2, shifting
two positions is equivalent to multiplying
by 4, etc.
Called Bitwise Shift Right with Sign
Operator. It moves all bits in its first
operand to the right by the number of
places specified in the second operand.
The bits filled in on the left depend on the
sign bit of the original operand, in order to
preserve the sign of the result. If the first
>> operand is positive, the result has zeros (A >> 1) is 1.
placed in the high bits; if the first operand
is negative, the result has ones placed in
the high bits. Shifting a value right one
place is equivalent to dividing by 2
(discarding the remainder), shifting right
two places is equivalent to integer division
by 4, and so on.
Called Bitwise Shift Right with Zero
Operator. This operator is just like the >>
>>> (A >>> 1) is 1.
operator, except that the bits shifted in on
the left are always zero,