Page 149 - DCAP208_Management Support Systems
P. 149
Management Support Systems
Notes Test marketing is an excellent source of data for this kind of modeling. Mining the results of a
test market representing a broad but relatively small sample of prospects can provide a foundation
for identifying good prospects in the overall market. Table 9.2 shows another common scenario
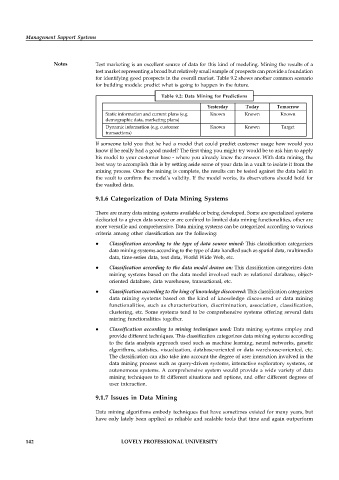
for building models: predict what is going to happen in the future.
Table 9.2: Data Mining for Predictions
Yesterday Today Tomorrow
Static information and current plans (e.g. Known Known Known
demographic data, marketing plans)
Dynamic information (e.g. customer Known Known Target
transactions)
If someone told you that he had a model that could predict customer usage how would you
know if he really had a good model? The first thing you might try would be to ask him to apply
his model to your customer base - where you already knew the answer. With data mining, the
best way to accomplish this is by setting aside some of your data in a vault to isolate it from the
mining process. Once the mining is complete, the results can be tested against the data held in
the vault to confirm the model’s validity. If the model works, its observations should hold for
the vaulted data.
9.1.6 Categorization of Data Mining Systems
There are many data mining systems available or being developed. Some are specialized systems
dedicated to a given data source or are confined to limited data mining functionalities, other are
more versatile and comprehensive. Data mining systems can be categorized according to various
criteria among other classification are the following:
Classification according to the type of data source mined: This classification categorizes
data mining systems according to the type of data handled such as spatial data, multimedia
data, time-series data, text data, World Wide Web, etc.
Classification according to the data model drawn on: This classification categorizes data
mining systems based on the data model involved such as relational database, object-
oriented database, data warehouse, transactional, etc.
Classification according to the king of knowledge discovered: This classification categorizes
data mining systems based on the kind of knowledge discovered or data mining
functionalities, such as characterization, discrimination, association, classification,
clustering, etc. Some systems tend to be comprehensive systems offering several data
mining functionalities together.
Classification according to mining techniques used: Data mining systems employ and
provide different techniques. This classification categorizes data mining systems according
to the data analysis approach used such as machine learning, neural networks, genetic
algorithms, statistics, visualization, database-oriented or data warehouse-oriented, etc.
The classification can also take into account the degree of user interaction involved in the
data mining process such as query-driven systems, interactive exploratory systems, or
autonomous systems. A comprehensive system would provide a wide variety of data
mining techniques to fit different situations and options, and offer different degrees of
user interaction.
9.1.7 Issues in Data Mining
Data mining algorithms embody techniques that have sometimes existed for many years, but
have only lately been applied as reliable and scalable tools that time and again outperform
142 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY