Page 243 - Open Soource Technologies 304.indd
P. 243
Open Source Technologies
Notes WHERE <conditions that data must satisfy>;
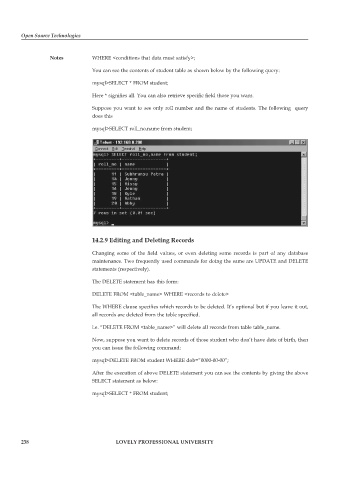
You can see the contents of student table as shown below by the following query:
mysql>SELECT * FROM student;
Here * signifies all. You can also retrieve specific field those you want.
Suppose you want to see only roll number and the name of students. The following query
does this
mysql>SELECT roll_no,name from student;
14.2.9 Editing and Deleting Records
Changing some of the field values, or even deleting some records is part of any database
maintenance. Two frequently used commands for doing the same are UPDATE and DELETE
statements (respectively).
The DELETE statement has this form:
DELETE FROM <table_name> WHERE <records to delete>
The WHERE clause specifies which records to be deleted. It’s optional but if you leave it out,
all records are deleted from the table specified.
i.e. “DELETE FROM <table_name>” will delete all records from table table_name.
Now, suppose you want to delete records of those student who don’t have date of birth, then
you can issue the following command:
mysql>DELETE FROM student WHERE dob=”0000-00-00”;
After the execution of above DELETE statement you can see the contents by giving the above
SELECT statement as below:
mysql>SELECT * FROM student;
238 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY