Page 84 - Open Soource Technologies 304.indd
P. 84
Unit 6: Building Blocks of PHP
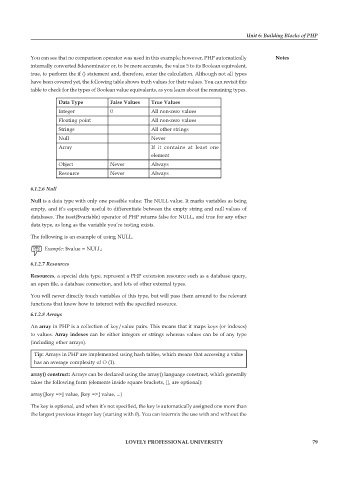
You can see that no comparison operator was used in this example; however, PHP automatically Notes
internally converted $denominator or, to be more accurate, the value 5 to its Boolean equivalent,
true, to perform the if () statement and, therefore, enter the calculation. Although not all types
have been covered yet, the following table shows truth values for their values. You can revisit this
table to check for the types of Boolean value equivalents, as you learn about the remaining types.
Data Type False Values True Values
Integer 0 All non-zero values
Floating point All non-zero values
Strings All other strings
Null Never
Array If it contains at least one
element
Object Never Always
Resource Never Always
6.1.2.6 Null
Null is a data type with only one possible value: The NULL value. It marks variables as being
empty, and it’s especially useful to differentiate between the empty string and null values of
databases. The isset($variable) operator of PHP returns false for NULL, and true for any other
data type, as long as the variable you’re testing exists.
The following is an example of using NULL.
Example: $value = NULL;
6.1.2.7 Resources
Resources, a special data type, represent a PHP extension resource such as a database query,
an open file, a database connection, and lots of other external types.
You will never directly touch variables of this type, but will pass them around to the relevant
functions that know how to interact with the specified resource.
6.1.2.8 Arrays
An array in PHP is a collection of key/value pairs. This means that it maps keys (or indexes)
to values. Array indexes can be either integers or strings whereas values can be of any type
(including other arrays).
Tip: Arrays in PHP are implemented using hash tables, which means that accessing a value
has an average complexity of O (1).
array() construct: Arrays can be declared using the array() language construct, which generally
takes the following form (elements inside square brackets, [], are optional):
array([key =>] value, [key =>] value, ...)
The key is optional, and when it’s not specified, the key is automatically assigned one more than
the largest previous integer key (starting with 0). You can intermix the use with and without the
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 79