Page 95 - Open Soource Technologies 304.indd
P. 95
Open Source Technologies
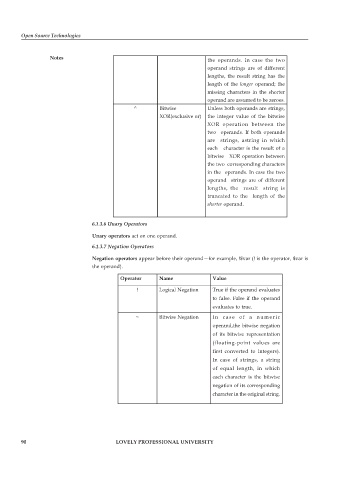
Notes the operands. In case the two
operand strings are of different
lengths, the result string has the
length of the longer operand; the
missing characters in the shorter
operand are assumed to be zeroes.
^ Bitwise Unless both operands are strings,
XOR(exclusive or) the integer value of the bitwise
XOR operation between the
two operands. If both operands
are strings, astring in which
each character is the result of a
bitwise XOR operation between
the two corresponding characters
in the operands. In case the two
operand strings are of different
lengths, the result string is
truncated to the length of the
shorter operand.
6.1.3.6 Unary Operators
Unary operators act on one operand.
6.1.3.7 Negation Operators
Negation operators appear before their operand—for example, !$var (! is the operator, $var is
the operand).
Operator Name Value
! Logical Negation True if the operand evaluates
to false. False if the operand
evaluates to true.
~ Bitwise Negation In case of a numeric
operand,the bitwise negation
of its bitwise representation
(floating-point values are
first converted to integers).
In case of strings, a string
of equal length, in which
each character is the bitwise
negation of its corresponding
character in the original string.
90 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY