Page 169 - DCAP206_INTRODUCTION_TO_COMPUTER_ORGANIZATION_AND_ARCHITECTURE_DCAP502_COMPUTER_ORGANIZATION_AND_ARCHITECTURE
P. 169
Computer Organization and Architecture/Introduction to Computer Organization and Architecture
Notes For convenience, the same symbol can be used for binary and decimal arithmetic micro-operations
with different interpretation. Table 10.2 depicts symbols for decimal arithmetic micro-operations.
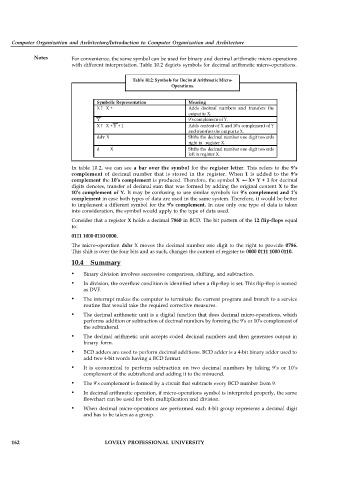
Table 10.2: Symbols for Decimal Arithmetic Micro-
Operations.
Symbolic Representation Meaning
X ? X + Adds decimal numbers and transfers the
output to X.
Y 9’s complement of Y.
X ? X + Y + 1 Adds content of X and 10's complement of Y
and transfers the output to X.
dshr X Shifts the decimal number one digit towards
right in register X.
d X Shifts the decimal number one digit towards
left in register X.
In table 10.2, we can see a bar over the symbol for the register letter. This refers to the 9’s
complement of decimal number that is stored in the register. When 1 is added to the 9’s
complement the 10’s complement is produced. Therefore, the symbol X X+ Y + 1 for decimal
digits denotes, transfer of decimal sum that was formed by adding the original content X to the
10’s complement of Y. It may be confusing to use similar symbols for 9’s complement and 1’s
complement in case both types of data are used in the same system. Therefore, it would be better
to implement a different symbol for the 9’s complement. In case only one type of data is taken
into consideration, the symbol would apply to the type of data used.
Consider that a register X holds a decimal 7860 in BCD. The bit pattern of the 12 flip-flops equal
to:
0111 1000 0110 0000.
The micro-operation dshr X moves the decimal number one digit to the right to provide 0786.
This shift is over the four bits and as such, changes the content of register to 0000 0111 1000 0110.
10.4 Summary
• Binary division involves successive comparison, shifting, and subtraction.
• In division, the overflow condition is identified when a flip-flop is set. This flip-flop is named
as DVF.
• The interrupt makes the computer to terminate the current program and branch to a service
routine that would take the required corrective measures.
• The decimal arithmetic unit is a digital function that does decimal micro-operations, which
performs addition or subtraction of decimal numbers by forming the 9’s or 10’s complement of
the subtrahend.
• The decimal arithmetic unit accepts coded decimal numbers and then generates output in
binary form.
• BCD adders are used to perform decimal additions. BCD adder is a 4-bit binary adder used to
add two 4-bit words having a BCD format.
• It is economical to perform subtraction on two decimal numbers by taking 9’s or 10’s
complement of the subtrahend and adding it to the minuend.
• The 9’s complement is formed by a circuit that subtracts every BCD number from 9.
• In decimal arithmetic operation, if micro-operations symbol is interpreted properly, the same
flowchart can be used for both multiplication and division.
• When decimal micro-operations are performed each 4-bit group represents a decimal digit
and has to be taken as a group.
162 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY