Page 58 - DCAP207_NETWORKS_DCAP406_COMPUTER_NETWORKS
P. 58
Unit 4: Physical Layer-2
Bandwidth: Satellites can support multiple transponders and, therefore, substantial Notes
bandwidth, with each transponder generally providing increments in bandwidth.
Error Performance: Satellite transmission is susceptible to environmental interference,
particularly at frequencies above 20 GHz. Sunspots and other types of electromagnetic
interference affect satellite and microwave transmission. Additionally, some satellite
frequency bands, for example, C–band needs careful frequency management. As a result
of these factors, satellite transmission often requires rather extensive error detection and
correction capabilities.
Distance: Satellite is not considered to be distance limited as the signal largely travels
through the vacuum of space. Further each signal travels approximately 36,000 kms in
each direction.
Propagation Delay: Geostationary satellites, by virtue of their high orbital altitude, impose
rather significant propagation delay on the signal. Hence, highly interactive voice, data,
and video applications are not effectively supported via two-way satellite communications.
Security: As is the case with all microwave and other radio systems, satellite transmission
is inherently not secure. Satellite transmission is especially vulnerable to interception, as
the signal is broadcast over the entire area of the footprint. Therefore, the unauthorized
user must know only the satellite and associated frequency range being employed. Security
must be imposed through encryption (scrambling) of the signal.
Cost: The acquisition, deployment, and rearrangement costs of the space segment of
satellite systems can be quite high in several million rupees. However, the satellite can be
shared by a large number of users, with each user perhaps connecting a large number of
sites. As a result, satellite networks often compare very favorably with cabled systems or
microwave systems for many point-to-multipoint applications.
Applications: Satellite applications are many and increasing rapidly as the traditional
voice and data services have been augmented. Traditional international voice and data
services have been supplanted to a considerable extent by submarine fiber optic cable
system.
Traditional, applications include international voice and data, remote voice and data, television
and radio broadcast, maritime navigation, videoconferencing, inventory management and
control through VSATs, disaster recovery and paging. More recent and emerging applications
include air navigation, Global Positioning Systems (GPS), mobile voice and data because of Low
Earth Orbit Satellites (LEOs), Advanced Traffic Management Systems (ATMS), Direct Broadcast
Satellite (DBS) TV, Integrated Digital Services Network (ISDN), interactive television, and
interactive multimedia.
Self Assessment
Match the following:
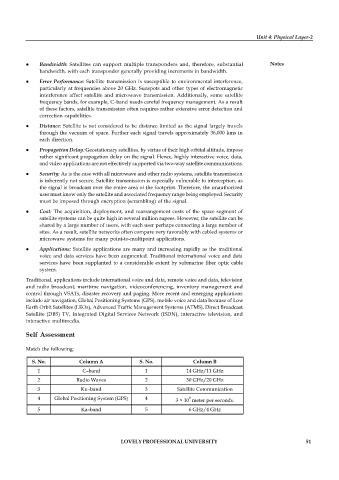
S. No. Column A S. No. Column B
1 C–band 1 14 GHz/11 GHz
2 Radio Waves 2 30 GHz/20 GHz
3 Ku–band 3 Satellite Communication
8
4 Global Positioning System (GPS) 4 3 × 10 meter per seconds.
5 Ka–band 5 6 GHz/4 GHz
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 51