Page 98 - DCAP207_NETWORKS_DCAP406_COMPUTER_NETWORKS
P. 98
Unit 6: Multiplexing
Notes
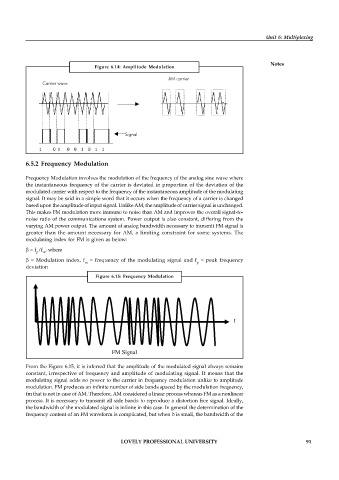
Figure 6.14: Amplitude Modulation
AM carrier
Carrier wave
Signal
6.5.2 Frequency Modulation
Frequency Modulation involves the modulation of the frequency of the analog sine wave where
the instantaneous frequency of the carrier is deviated in proportion of the deviation of the
modulated carrier with respect to the frequency of the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating
signal. It may be said in a simple word that it occurs when the frequency of a carrier is changed
based upon the amplitude of input signal. Unlike AM, the amplitude of carrier signal is unchanged.
This makes FM modulation more immune to noise than AM and improves the overall signal-to-
noise ratio of the communications system. Power output is also constant, differing from the
varying AM power output. The amount of analog bandwidth necessary to transmit FM signal is
greater than the amount necessary for AM, a limiting constraint for some systems. The
modulating index for FM is given as below:
β = f /f , where
p m
β = Modulation index, f = frequency of the modulating signal and f = peak frequency
m p
deviation
Figure 6.15: Frequency Modulation
t
FM Signal
From the Figure 6.15, it is inferred that the amplitude of the modulated signal always remains
constant, irrespective of frequency and amplitude of modulating signal. It means that the
modulating signal adds no power to the carrier in frequency modulation unlike to amplitude
modulation. FM produces an infinite number of side bands spaced by the modulation frequency,
fm that is not in case of AM. Therefore, AM considered a linear process whereas FM as a nonlinear
process. It is necessary to transmit all side bands to reproduce a distortion free signal. Ideally,
the bandwidth of the modulated signal is infinite in this case. In general the determination of the
frequency content of an FM waveform is complicated, but when b is small, the bandwidth of the
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 91