Page 42 - DCAP302_ENTERPRISE_RESOURCE_PLANNING
P. 42
Enterprise Resource Planning
notes example, rather than storing the details of each sales transaction, the data warehouse may store
a summary of the transactions per item type for each store or, summarised to a higher level, for
each sales region.
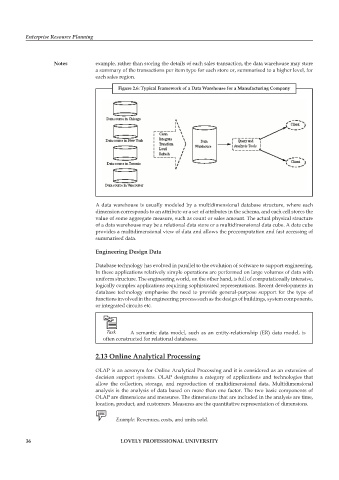
figure 2.6: typical framework of a Data Warehouse for a manufacturing company
A data warehouse is usually modeled by a multidimensional database structure, where each
dimension corresponds to an attribute or a set of attributes in the schema, and each cell stores the
value of some aggregate measure, such as count or sales amount. The actual physical structure
of a data warehouse may be a relational data store or a multidimensional data cube. A data cube
provides a multidimensional view of data and allows the precomputation and fast accessing of
summarised data.
engineering Design Data
Database technology has evolved in parallel to the evolution of software to support engineering.
In these applications relatively simple operations are performed on large volumes of data with
uniform structure. The engineering world, on the other hand, is full of computationally intensive,
logically complex applications requiring sophisticated representations. Recent developments in
database technology emphasise the need to provide general-purpose support for the type of
functions involved in the engineering process such as the design of buildings, system components,
or integrated circuits etc.
Task A semantic data model, such as an entity-relationship (ER) data model, is
often constructed for relational databases.
2.13 online analytical processing
OLAP is an acronym for Online Analytical Processing and it is considered as an extension of
decision support systems. OLAP designates a category of applications and technologies that
allow the collection, storage, and reproduction of multidimensional data. Multidimensional
analysis is the analysis of data based on more than one factor. The two basic components of
OLAP are dimensions and measures. The dimensions that are included in the analysis are time,
location, product, and customers. Measures are the quantitative representation of dimensions.
Example: Revenues, costs, and units sold.
36 LoveLy professionaL university