Page 56 - DCAP303_MULTIMEDIA_SYSTEMS
P. 56
Multimedia Systems
notes There are other methods of converting bitmaps of high colour depth into those of lower colour depth
but higher resolution, on such technique used in the printing industry is called screening. Screening
will not be discussed here except to say that it approximates grey levels by different size objects (the
size of the object is proportional to the grey level) the objects are arranged on in a regular matrix
which is at some angle to the horizontal. The most commonly used imaging objects are dots, lines
and rectangles. Figure 4.14 shows a grey level ramp with the corresponding black and white screened
examples (greatly enlarged) using dot and line screens.
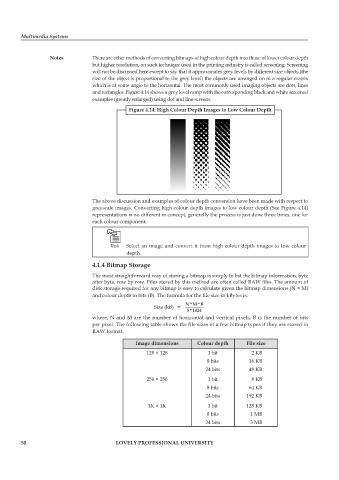
figure 4.14: High Colour Depth images to Low Colour Depth
The above discussion and examples of colour depth conversion have been made with respect to
greyscale images. Converting high colour depth images to low colour depth (See Figure 4.14)
representations is no different in concept, generally the process is just done three times, one for
each colour component.
Select an image and convert it from high colour depth images to low colour
depth.
4.1.4 Bitmap storage
The most straightforward way of storing a bitmap is simply to list the bitmap information, byte
after byte, row by row. Files stored by this method are often called RAW files. The amount of
disk storage required for any bitmap is easy to calculate given the bitmap dimensions (N × M)
and colour depth in bits (B). The formula for the file size in kBytes is:
*
*
Size (kB) = NM B
8 * 1024
where, N and M are the number of horizontal and vertical pixels, B is the number of bits
per pixel. The following table shows the file sizes of a few bitmap types if they are stored in
RAW format.
image dimensions Colour depth file size
128 × 128 1 bit 2 KB
8 bits 16 KB
24 bits 48 KB
256 × 256 1 bit 8 KB
8 bits 64 KB
24 bits 192 KB
1K × 1K 1 bit 128 KB
8 bits 1 MB
24 bits 3 MB
50 LoveLy professionaL University