Page 116 - DCAP305_PRINCIPLES_OF_SOFTWARE_ENGINEERING
P. 116
Principles of Software Engineering
Notes exist, there may be no known identifiers for them. Instead, we must represent a derived object
with a descriptor that will cause the object to be generated when it is needed. This descriptor
must specify not only the derivers, but all parameter settings for the derivers as well.
For clarity, we should point out some uses of the above definitions. Suppose a software house
delivers a single, binary program to a customer. This program is a single, derived object. It
most cases, this object was generated from a baseline configuration recorded at the software
house. The purpose of the baseline is to guarantee that the derived object can be reproduced
when needed. The software house may also deliver a configuration, perhaps a composite that
consists of one or more binaries and a manual. The delivered configuration may also contain
source programs, because the programs will be interpreted, or because the customer wishes to
compile source locally. The customer may also need to adapt the source code to local needs. Thus,
depending on how much the customer expects to do, a more or less complete SCM system must
be available at the customer site to take over portions of the software house’s SCM functions.
5.8 Quality Plan
A quality plan describes how an organisation will achieve its quality objectives. It describes the
quality objectives and specifies the quality assurance and control activities to be performed in
day-to-day company operations. In the case of a software development organisation individual
quality plans may be prepared for each software or systems engineering project.
ISO 9001 requires top management to “ensure that the planning of the quality management
system is carried out.”
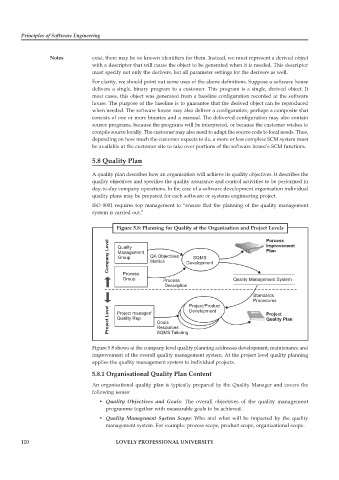
Figure 5.8: Planning for Quality at the Organisation and Project Levels
Porcess
Company Level Quality QA Objectives Development Improvement
Plan
Management
Group
SQMS
Metrics
Process
Group Process Quality Management System
Description
Standards
Procedures
Project/Product
Project Level Project manager/ Goals Development Project
Quality Rep.
Quality Plan
Resources
SQMS Tailoring
Figure 5.8 shows at the company level quality planning addresses development, maintenance and
improvement of the overall quality management system. At the project level quality planning
applies the quality management system to individual projects.
5.8.1 Organisational Quality Plan Content
An organisational quality plan is typically prepared by the Quality Manager and covers the
following issues:
• Quality Objectives and Goals: The overall objectives of the quality management
programme together with measurable goals to be achieved.
• Quality Management System Scope: Who and what will be impacted by the quality
management system. For example: process scope, product scope, organizational scope.
110 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY