Page 36 - DCAP305_PRINCIPLES_OF_SOFTWARE_ENGINEERING
P. 36
Principles of Software Engineering
Notes essential features of a later system is the most appropriate definition of a prototype. A prototype
system, intentionally incomplete, is to be modified, supplemented, or supplanted.
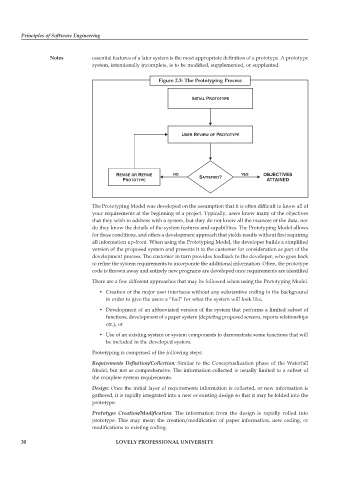
Figure 2.3: The Prototyping Process
The Prototyping Model was developed on the assumption that it is often difficult to know all of
your requirements at the beginning of a project. Typically, users know many of the objectives
that they wish to address with a system, but they do not know all the nuances of the data, nor
do they know the details of the system features and capabilities. The Prototyping Model allows
for these conditions, and offers a development approach that yields results without first requiring
all information up-front. When using the Prototyping Model, the developer builds a simplified
version of the proposed system and presents it to the customer for consideration as part of the
development process. The customer in turn provides feedback to the developer, who goes back
to refine the system requirements to incorporate the additional information. Often, the prototype
code is thrown away and entirely new programs are developed once requirements are identified
There are a few different approaches that may be followed when using the Prototyping Model.
• Creation of the major user interfaces without any substantive coding in the background
in order to give the users a “feel” for what the system will look like,
• Development of an abbreviated version of the system that performs a limited subset of
functions; development of a paper system (depicting proposed screens, reports relationships
etc.), or
• Use of an existing system or system components to demonstrate some functions that will
be included in the developed system.
Prototyping is comprised of the following steps:
Requirements Definition/Collection: Similar to the Conceptualization phase of the Waterfall
Model, but not as comprehensive. The information collected is usually limited to a subset of
the complete system requirements.
Design: Once the initial layer of requirements information is collected, or new information is
gathered, it is rapidly integrated into a new or existing design so that it may be folded into the
prototype.
Prototype Creation/Modification: The information from the design is rapidly rolled into
prototype. This may mean the creation/modification of paper information, new coding, or
modifications to existing coding.
30 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY