Page 44 - DCAP305_PRINCIPLES_OF_SOFTWARE_ENGINEERING
P. 44
Principles of Software Engineering
Notes 2.7 Comparison Process Models
The comparison between various process models is given in Table 2.1.
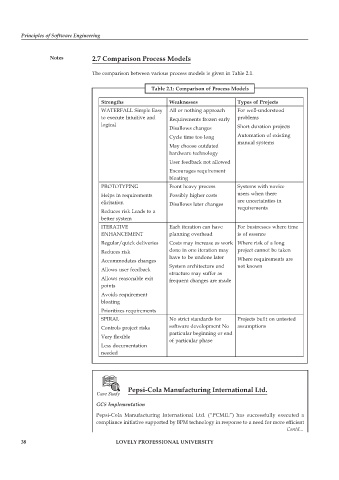
Table 2.1: Comparison of Process Models
Strengths Weaknesses Types of Projects
WATERFALL Simple Easy All or nothing approach For well-understood
to execute Intuitive and Requirements frozen early problems
logical Short duration projects
Disallows changes
Cycle time too long Automation of existing
manual systems
May choose outdated
hardware technology
User feedback not allowed
Encourages requirement
bloating
PROTOTYPING Front heavy process Systems with novice
Helps in requirements Possibly higher costs users when there
elicitation Disallows later changes are uncertainties in
Reduces risk Leads to a requirements
better system
ITERATIVE Each iteration can have For businesses where time
ENHANCEMENT planning overhead is of essence
Regular/quick deliveries Costs may increase as work Where risk of a long
Reduces risk done in one iteration may project cannot be taken
have to be undone later
Accommodates changes Where requirements are
Allows user feedback System architecture and not known
structure may suffer as
Allows reasonable exit frequent changes are made
points
Avoids requirement
bloating
Prioritizes requirements
SPIRAL No strict standards for Projects built on untested
Controls project risks software development No assumptions
Very flexible particular beginning or end
of particular phase
Less documentation
needed
Pepsi-Cola Manufacturing International Ltd.
GCS Implementation
Pepsi-Cola Manufacturing International Ltd. (“PCMIL”) has successfully executed a
compliance initiative supported by BPM technology in response to a need for more efficient
Contd...
38 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY