Page 118 - DCAP308_OBJECT_ORIENTED_ANALYSIS_AND_DESIGN
P. 118
Object Oriented Analysis and Design
Notes Software engineers have developed a number of different ‘life styles’ through which software
passes. In general these life styles are known as software development life cycle or SDLC in
short.
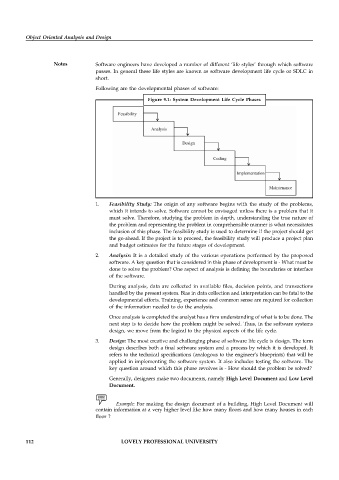
Following are the developmental phases of software:
Figure 9.1: System Development Life Cycle Phases
1. Feasibility Study: The origin of any software begins with the study of the problems,
which it intends to solve. Software cannot be envisaged unless there is a problem that it
must solve. Therefore, studying the problem in depth, understanding the true nature of
the problem and representing the problem in comprehensible manner is what necessitates
inclusion of this phase. The feasibility study is used to determine if the project should get
the go-ahead. If the project is to proceed, the feasibility study will produce a project plan
and budget estimates for the future stages of development.
2. Analysis: It is a detailed study of the various operations performed by the proposed
software. A key question that is considered in this phase of development is - What must be
done to solve the problem? One aspect of analysis is defining the boundaries or interface
of the software.
During analysis, data are collected in available files, decision points, and transactions
handled by the present system. Bias in data collection and interpretation can be fatal to the
developmental efforts. Training, experience and common sense are required for collection
of the information needed to do the analysis.
Once analysis is completed the analyst has a firm understanding of what is to be done. The
next step is to decide how the problem might be solved. Thus, in the software systems
design, we move from the logical to the physical aspects of the life cycle.
3. Design: The most creative and challenging phase of software life cycle is design. The term
design describes both a final software system and a process by which it is developed. It
refers to the technical specifications (analogous to the engineer’s blueprints) that will be
applied in implementing the software system. It also includes testing the software. The
key question around which this phase revolves is - How should the problem be solved?
Generally, designers make two documents, namely High Level Document and Low Level
Document.
Example: For making the design document of a building, High Level Document will
contain information at a very higher level like how many floors and how many houses in each
floor ?
112 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY