Page 62 - DCAP308_OBJECT_ORIENTED_ANALYSIS_AND_DESIGN
P. 62
Object Oriented Analysis and Design
Notes
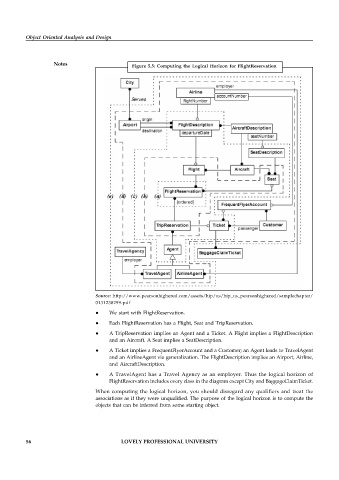
Figure 5.5: Computing the Logical Horizon for FlightReservation
Source: http://www.pearsonhighered.com/assets/hip/us/hip_us_pearsonhighered/samplechapter/
0131238299.pdf
We start with FlightReservation.
Each FlightReservation has a Flight, Seat and TripReservation.
A TripReservation implies an Agent and a Ticket. A Flight implies a FlightDescription
and an Aircraft. A Seat implies a SeatDescription.
A Ticket implies a FrequentFlyerAccount and a Customer; an Agent leads to TravelAgent
and an AirlineAgent via generalization. The FlightDescription implies an Airport, Airline,
and AircraftDescription.
A TravelAgent has a Travel Agency as an employer. Thus the logical horizon of
FlightReservation includes every class in the diagram except City and BaggageClaimTicket.
When computing the logical horizon, you should disregard any qualifiers and treat the
associations as if they were unqualified. The purpose of the logical horizon is to compute the
objects that can be inferred from some starting object.
56 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY