Page 128 - DCAP309_INFORMATION_SECURITY_AND_PRIVACY
P. 128
Information Security and Privacy
Notes
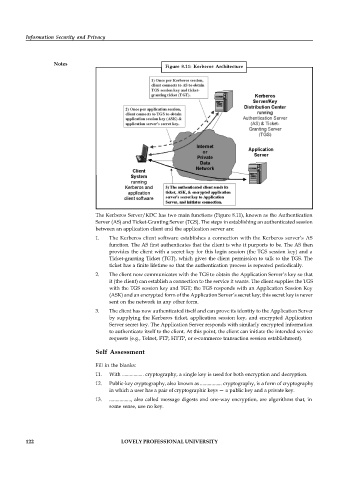
Figure 8.11: Kerberos Architecture
The Kerberos Server/KDC has two main functions (Figure 8.11), known as the Authentication
Server (AS) and Ticket-Granting Server (TGS). The steps in establishing an authenticated session
between an application client and the application server are:
1. The Kerberos client software establishes a connection with the Kerberos server’s AS
function. The AS first authenticates that the client is who it purports to be. The AS then
provides the client with a secret key for this login session (the TGS session key) and a
Ticket-granting Ticket (TGT), which gives the client permission to talk to the TGS. The
ticket has a finite lifetime so that the authentication process is repeated periodically.
2. The client now communicates with the TGS to obtain the Application Server’s key so that
it (the client) can establish a connection to the service it wants. The client supplies the TGS
with the TGS session key and TGT; the TGS responds with an Application Session Key
(ASK) and an encrypted form of the Application Server’s secret key; this secret key is never
sent on the network in any other form.
3. The client has now authenticated itself and can prove its identity to the Application Server
by supplying the Kerberos ticket, application session key, and encrypted Application
Server secret key. The Application Server responds with similarly encrypted information
to authenticate itself to the client. At this point, the client can initiate the intended service
requests (e.g., Telnet, FTP, HTTP, or e-commerce transaction session establishment).
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
11. With ................. cryptography, a single key is used for both encryption and decryption.
12. Public-key cryptography, also known as ................. cryptography, is a form of cryptography
in which a user has a pair of cryptographic keys — a public key and a private key.
13. ................., also called message digests and one-way encryption, are algorithms that, in
some sense, use no key.
122 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY