Page 36 - DCAP101_BASIC_COMPUTER_SKILLS
P. 36
Unit 2: Introduction to Data Representations
Step 2: Combine the binary groups. Notes
0010 0010 1011
2AB =
16
2 A B
Hence, 2AB = 001010101011
16 2
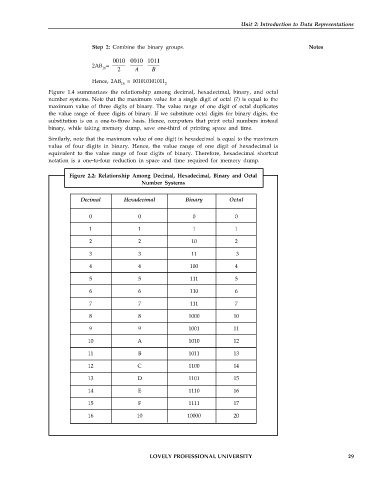
Figure 1.4 summarizes the relationship among decimal, hexadecimal, binary, and octal
number systems. Note that the maximum value for a single digit of octal (7) is equal to the
maximum value of three digits of binary. The value range of one digit of octal duplicates
the value range of three digits of binary. If we substitute octal digits for binary digits, the
substitution is on a one-to-three basis. Hence, computers that print octal numbers instead
binary, while taking memory dump, save one-third of printing space and time.
Similarly, note that the maximum value of one digit in hexadecimal is equal to the maximum
value of four digits in binary. Hence, the value range of one digit of hexadecimal is
equivalent to the value range of four digits of binary. Therefore, hexadecimal shortcut
notation is a one-to-four reduction in space and time required for memory dump.
Figure 2.2: Relationship Among Decimal, Hexadecimal, Binary and Octal
Number Systems
Decimal Hexadecimal Binary Octal
0 0 0 0
1 1 1 1
2 2 10 2
3 3 11 3
4 4 100 4
5 5 111 5
6 6 110 6
7 7 111 7
8 8 1000 10
9 9 1001 11
10 A 1010 12
11 B 1011 13
12 C 1100 14
13 D 1101 15
14 E 1110 16
15 F 1111 17
16 10 10000 20
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 29