Page 43 - DCAP101_BASIC_COMPUTER_SKILLS
P. 43
Basic Computer Skills
Notes microseconds/byte. Hence, within the time in which a disk can supply one byte of data
a CPU can process 1000 bytes. This would lead to a very slow overall performance even
if a computer used a very fast CPU. To overcome this problem, there is a need to have
a reasonably large storage space that can hold the instructions and data of the program(s)
on which CPU is currently working time to fetch and load data from this storage space
into CPU registers must also be very small as compared to that space from disk storage
to reduce the speed mismatch problem with CPU speed. Every computer has such a storage
space known as primary storage, main memory, or simply memory. It is a temporary
storage area built into the computer hardware. Instructions and data of a program reside
mainly in this area when CPU is executing the program. Physically, this memory consists
of some integrated circuit (IC) chips either on the motherboard or on a small circuit board
attached to the motherboard of a computer system. This built-in memory allows CPU to
store and retrieve data very quickly. The rate of fetching data from this memory is of the
order of 50 nanoseconds/byte. Hence, the rate of data fetching from main memory is about
100 times faster than that from a high speed secondary storage like disk.
3.1 Unit of Memory
Starting with the Unit of memory, you can see the difference between things like a “Kilobyte”
and a “Megabyte” and other computer memory terms.
The charts below will give you a clear understanding of:
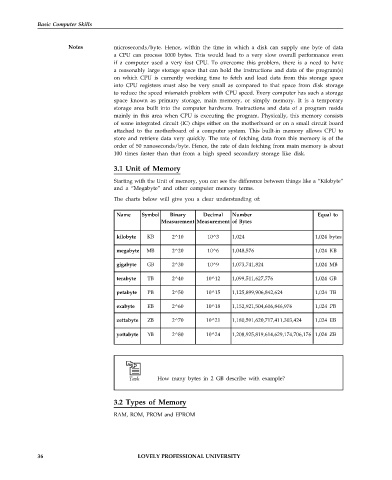
Name Symbol Binary Decimal Number Equal to
Measurement Measurement of Bytes
kilobyte KB 2^10 10^3 1,024 1,024 bytes
megabyte MB 2^20 10^6 1,048,576 1,024 KB
gigabyte GB 2^30 10^9 1,073,741,824 1,024 MB
terabyte TB 2^40 10^12 1,099,511,627,776 1,024 GB
petabyte PB 2^50 10^15 1,125,899,906,842,624 1,024 TB
exabyte EB 2^60 10^18 1,152,921,504,606,846,976 1,024 PB
zettabyte ZB 2^70 10^21 1,180,591,620,717,411,303,424 1,024 EB
yottabyte YB 2^80 10^24 1,208,925,819,614,629,174,706,176 1,024 ZB
How many bytes in 2 GB describe with example?
3.2 Types of Memory
RAM, ROM, PROM and EPROM
36 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY