Page 265 - DCAP103_Principle of operating system
P. 265
Principles of Operating Systems
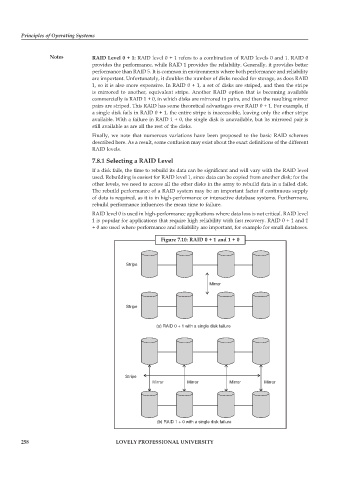
Notes RAID Level 0 + 1: RAID level 0 + 1 refers to a combination of RAID levels 0 and 1. RAID 0
provides the performance, while RAID 1 provides the reliability. Generally, it provides better
performance than RAID 5. It is common in environments where both performance and reliability
are important. Unfortunately, it doubles the number of disks needed for storage, as does RAID
1, so it is also more expensive. In RAID 0 + 1, a set of disks are striped, and then the stripe
is mirrored to another, equivalent stripe. Another RAID option that is becoming available
commercially is RAID 1 + 0, in which disks are mirrored in pairs, and then the resulting mirror
pairs are striped. This RAID has some theoretical advantages over RAID 0 + 1. For example, if
a single disk fails in RAID 0 + 1, the entire stripe is inaccessible, leaving only the other stripe
available. With a failure in RAID 1 + 0, the single disk is unavailable, but its mirrored pair is
still available as are all the rest of the disks.
Finally, we note that numerous variations have been proposed to the basic RAID schemes
described here. As a result, some confusion may exist about the exact definitions of the different
RAID levels.
7.8.1 Selecting a RAID Level
If a disk fails, the time to rebuild its data can be significant and will vary with the RAID level
used. Rebuilding is easiest for RAID level 1, since data can be copied from another disk; for the
other levels, we need to access all the other disks in the array to rebuild data in a failed disk.
The rebuild performance of a RAID system may be an important factor if continuous supply
of data is required, as it is in high-performance or interactive database systems. Furthermore,
rebuild performance influences the mean time to failure.
RAID level 0 is used in high-performance applications where data loss is not critical. RAID level
1 is popular for applications that require high reliability with fast recovery. RAID 0 + 1 and 1
+ 0 are used where performance and reliability are important, for example for small databases.
Figure 7.10: RAID 0 + 1 and 1 + 0
Stripe
Mirror
Stripe
(a) RAID0+1 witha single disk failure
Stripe
Mirror Mirror Mirror Mirror
(b) RAID1+0 witha single disk failure
258 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY