Page 37 - DCAP103_Principle of operating system
P. 37
Principles of Operating Systems
Notes Software Implementation Issues
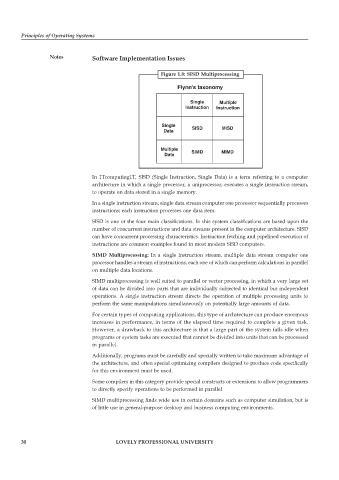
Figure 1.8: SISD Multiprocessing
In 1Tcomputing1T, SISD (Single Instruction, Single Data) is a term referring to a computer
architecture in which a single processor, a uniprocessor, executes a single instruction stream,
to operate on data stored in a single memory.
In a single instruction stream, single data stream computer one processor sequentially processes
instructions; each instruction processes one data item.
SISD is one of the four main classifications. In this system classifications are based upon the
number of concurrent instructions and data streams present in the computer architecture. SISD
can have concurrent processing characteristics. Instruction fetching and pipelined execution of
instructions are common examples found in most modern SISD computers.
SIMD Multiprocessing: In a single instruction stream, multiple data stream computer one
processor handles a stream of instructions, each one of which can perform calculations in parallel
on multiple data locations.
SIMD multiprocessing is well suited to parallel or vector processing, in which a very large set
of data can be divided into parts that are individually subjected to identical but independent
operations. A single instruction stream directs the operation of multiple processing units to
perform the same manipulations simultaneously on potentially large amounts of data.
For certain types of computing applications, this type of architecture can produce enormous
increases in performance, in terms of the elapsed time required to complete a given task.
However, a drawback to this architecture is that a large part of the system falls idle when
programs or system tasks are executed that cannot be divided into units that can be processed
in parallel.
Additionally, programs must be carefully and specially written to take maximum advantage of
the architecture, and often special optimizing compilers designed to produce code specifically
for this environment must be used.
Some compilers in this category provide special constructs or extensions to allow programmers
to directly specify operations to be performed in parallel.
SIMD multiprocessing finds wide use in certain domains such as computer simulation, but is
of little use in general-purpose desktop and business computing environments.
30 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY