Page 100 - DCAP104_EXPOSURE_TO_COMPUTER_DISCPLINES
P. 100
Unit 5: Operations of Network
While grid networks have found popularity in high-performance computing applications, some Notes
systems have used genetic algorithms to design custom networks that have the fewest possible
hops in between different nodes. Some of the resulting layouts are nearly incomprehensible,
although they function quite well.
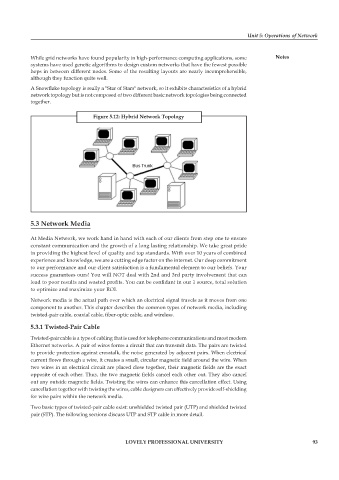
A Snowflake topology is really a "Star of Stars" network, so it exhibits characteristics of a hybrid
network topology but is not composed of two different basic network topologies being connected
together.
Figure 5.12: Hybrid Network Topology
5.3 Network Media
At Media Network, we work hand in hand with each of our clients from step one to ensure
constant communication and the growth of a long lasting relationship. We take great pride
in providing the highest level of quality and top standards. With over 10 years of combined
experience and knowledge, we are a cutting edge factor on the internet. Our deep commitment
to our performance and our client satisfaction is a fundamental element to our beliefs. Your
success guarantees ours! You will NOT deal with 2nd and 3rd party involvement that can
lead to poor results and wasted profits. You can be confidant in our 1 source, total solution
to optimize and maximize your ROI.
Network media is the actual path over which an electrical signal travels as it moves from one
component to another. This chapter describes the common types of network media, including
twisted-pair cable, coaxial cable, fiber-optic cable, and wireless.
5.3.1 Twisted-Pair Cable
Twisted-pair cable is a type of cabling that is used for telephone communications and most modern
Ethernet networks. A pair of wires forms a circuit that can transmit data. The pairs are twisted
to provide protection against crosstalk, the noise generated by adjacent pairs. When electrical
current flows through a wire, it creates a small, circular magnetic field around the wire. When
two wires in an electrical circuit are placed close together, their magnetic fields are the exact
opposite of each other. Thus, the two magnetic fields cancel each other out. They also cancel
out any outside magnetic fields. Twisting the wires can enhance this cancellation effect. Using
cancellation together with twisting the wires, cable designers can effectively provide self-shielding
for wire pairs within the network media.
Two basic types of twisted-pair cable exist: unshielded twisted pair (UTP) and shielded twisted
pair (STP). The following sections discuss UTP and STP cable in more detail.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 93