Page 23 - DCAP104_EXPOSURE_TO_COMPUTER_DISCPLINES
P. 23
Exposure to Computer Disciplines
Notes Objectives
After studying this unit, you will be able to:
• Explain data processing cycle.
• Discuss data processing system.
• Explain machine cycle.
• Explain different types of memory.
• Discuss different registers.
• Explain computer bus.
• Discuss cache memory in detail.
2.1 Method of Processing Data
Data processing consists of those activities which are necessary to transform data into information.
Man has in course of time devised certain tools to help him in processing data. These include
manual tools such as pencil and paper, mechanical tools such as filing cabinets, electromechanical
tools such as adding machines and typewriters, and electronic tools such as calculators and
computers. Many people immediately associate data processing with computers.
Processing is the thinking that the computer does - the calculations, comparisons, and decisions.
People also process data. What you see and hear and touch and feel is input. Then you connect
this new input with what you already know, look for how it all fits together, and come up with
a reaction, your output. “That stove is hot. I’ll move my hand now!”
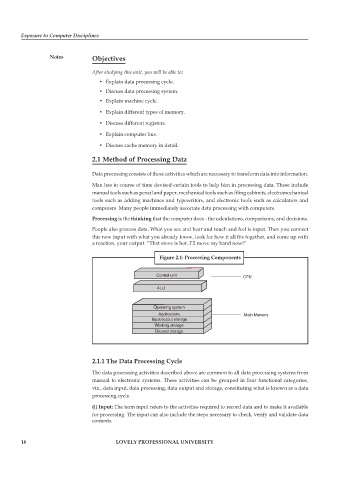
Figure 2.1: Processing Components
2.1.1 The Data Processing Cycle
The data processing activities described above are common to all data processing systems from
manual to electronic systems. These activities can be grouped in four functional categories,
viz., data input, data processing, data output and storage, constituting what is known as a data
processing cycle.
(i) Input: The term input refers to the activities required to record data and to make it available
for processing. The input can also include the steps necessary to check, verify and validate data
contents.
16 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY