Page 179 - DCAP106_OPERATING_SYSTEM_TOOLS
P. 179
Operating System Tools
Notes There can be uncertainty with the locations: Regular BIND installs its files in the normal
locations, and the chroot BIND add-on RPM installs its own versions in their chroot
locations. Unfortunately, the chroot versions of some of the files are empty. Before starting
Fedora BIND, copy the configuration files to their chroot locations:
[root@bigboy tmp]# cp -f /etc/named.conf /var/named/chroot/etc/
[root@bigboy tmp]# cp -f /etc/rndc.* /var/named/chroot/etc/
Before you go to the next step of configuring a regular name server, it is important to
understand exactly where the files are located.
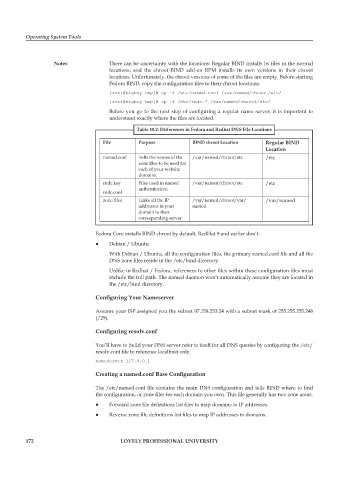
Table 10.2: Differences in Fedora and Redhat DNS File Locations
File Purpose BIND chroot Location Regular BIND
Location
named.conf Tells the names of the /var/named/chroot/etc /etc
zone files to be used for
each of your website
domains.
rndc.key Files used in named /var/named/chroot/etc /etc
authentication
rndc.conf
zone files Links all the IP /var/named/chroot/var/ /var/named
addresses in your named
domain to their
corresponding server
Fedora Core installs BIND chroot by default. RedHat 9 and earlier don’t.
z z Debian / Ubuntu
With Debian / Ubuntu, all the configuration files, the primary named.conf file and all the
DNS zone files reside in the /etc/bind directory.
Unlike in Redhat / Fedora, references to other files within these configuration files must
include the full path. The named daemon won’t automatically assume they are located in
the /etc/bind directory.
Configuring Your Nameserver
Assume your ISP assigned you the subnet 97.158.253.24 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.248
(/29).
Configuring resolv.conf
You’ll have to build your DNS server refer to itself for all DNS queries by configuring the /etc/
resolv.conf file to reference localhost only.
nameserver 127.0.0.1
Creating a named.conf Base Configuration
The /etc/named.conf file contains the main DNS configuration and tells BIND where to find
the configuration, or zone files for each domain you own. This file generally has two zone areas:
z z Forward zone file definitions list files to map domains to IP addresses.
z z Reverse zone file definitions list files to map IP addresses to domains.
172 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY