Page 13 - DCAP404 _Object Oriented Programming
P. 13
Object-oriented Programming
Notes As is evident from the ongoing discussion, object-oriented approach deals with objects
and classes as against series of functions and as actions adopted by procedural approach.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
1. Each object contains data and ………………… to manipulate the data.
2. ……………………. have an interface that defines which part of an object of a class can be
accessed from outside and how.
3. The power of inheritance lies in the fact that all common features of the subclasses can be
accumulated in the ………………… class.
4. At run-time, the code matching the ………………… under reference will be called.
1.2 Introduction to OOP Languages
Object oriented programming is not the right of any particular language. Although languages
like C and Pascal can be used but programming becomes clumsy and may generate confusion
when program grow in size. A language that is specially designed to support the OOP concepts
makes it easier to implement them.
To claim that they are object-oriented they should support several concepts of OOP.
Depending upon the features they support, they are classified into the following categories:
1. Object-based programming languages.
2. Object-oriented programming languages.
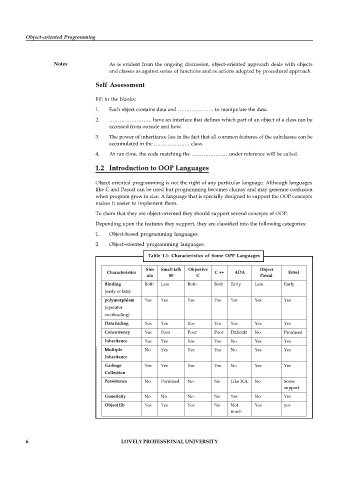
Table 1.1: Characteristics of Some OPP Languages
Sim Small talk Objective Object
Characteristics C ++ ADA Eittel
ula 80 C Pascal
Binding Both Late Both Both Early Late Early
(early or late)
polymorphism Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
(operator
overloading)
Data hiding Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Concurrency Yes Poor Poor Poor Difficult No Promised
Inheritance Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes Yes
Multiple No Yes Yes Yes No Yes Yes
Inheritance
Garbage Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes Yes
Collection
Persistence No Pormised No No Like 3GL No Some
support
Genericity No No No No Yes No Yes
Object lib Yes Yes Yes No Not Yes yes
much
6 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY