Page 67 - DCAP109_GRAPHIC_TOOLS
P. 67
Graphic Tools
Notes
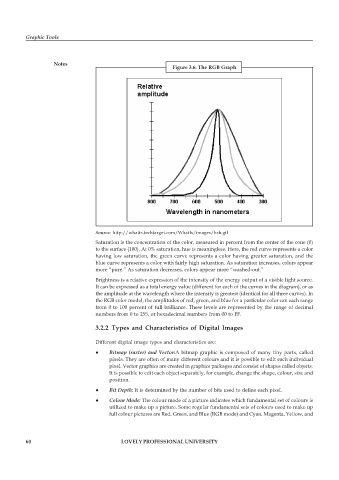
Figure 3.6: The RGB Graph
Source: http://whatis.techtarget.com/WhatIs/images/hsb.gif
Saturation is the concentration of the color, measured in percent from the center of the cone (0)
to the surface (100). At 0% saturation, hue is meaningless. Here, the red curve represents a color
having low saturation, the green curve represents a color having greater saturation, and the
blue curve represents a color with fairly high saturation. As saturation increases, colors appear
more “pure.” As saturation decreases, colors appear more “washed-out.”
Brightness is a relative expression of the intensity of the energy output of a visible light source.
It can be expressed as a total energy value (different for each of the curves in the diagram), or as
the amplitude at the wavelength where the intensity is greatest (identical for all three curves). In
the RGB color model, the amplitudes of red, green, and blue for a particular color can each range
from 0 to 100 percent of full brilliance. These levels are represented by the range of decimal
numbers from 0 to 255, or hexadecimal numbers from 00 to FF.
3.2.2 Types and Characteristics of Digital Images
Different digital image types and characteristics are:
z Bitmap (raster) and Vector:A bitmap graphic is composed of many tiny parts, called
pixels. They are often of many different colours and it is possible to edit each individual
pixel. Vector graphics are created in graphics packages and consist of shapes called objects.
It is possible to edit each object separately, for example, change the shape, colour, size and
position.
z Bit Depth: It is determined by the number of bits used to define each pixel.
z Colour Mode: The colour mode of a picture indicates which fundamental set of colours is
utilized to make up a picture. Some regular fundamental sets of colours used to make up
full colour pictures are Red, Green, and Blue (RGB mode) and Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and
60 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY