Page 109 - DCAP201_FUNDAMENTALS_OF_DATA_STRUCTURES
P. 109
Fundamentals of Data Structures
Notes Application of Circular Linked List
A famous problem that uses a circularly linked list is the Josephus problem. This problem has to
do with selective deletion from a circularly linked list. There is a group of bandits in the Wild
West who find themselves in a desperate predicament. The group is surrounded by the sheriff’s
posse and has no hope for mass escape. There is just one horse left. In order to select who shall
take the horse and ride off with the booty, then do the following. Numbers are written on slips
of paper and shuffled in a hat. The bandits stand in a circle. One is designed to be in the starting
position.
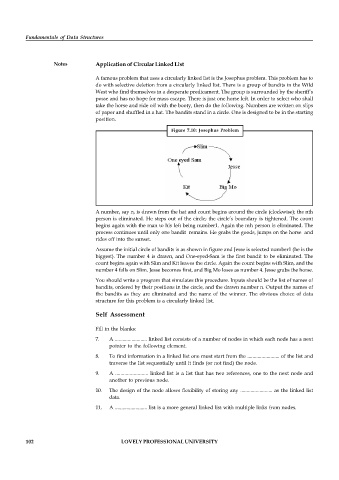
Figure 7.10: Josephus Problem
A number, say n, is drawn from the hat and count begins around the circle (clockwise); the nth
person is eliminated. He steps out of the circle; the circle’s boundary is tightened. The count
begins again with the man to his left being number1. Again the nth person is eliminated. The
process continues until only one bandit remains. He grabs the goods, jumps on the horse and
rides off into the sunset.
Assume the initial circle of bandits is as shown in figure and Jesse is selected number1 (he is the
biggest). The number 4 is drawn, and One-eyed-Sam is the first bandit to be eliminated. The
count begins again with Slim and Kit leaves the circle. Again the count begins with Slim, and the
number 4 falls on Slim. Jesse becomes first, and Big Mo loses as number 4. Jesse grabs the horse.
You should write a program that simulates this procedure. Inputs should be the list of names of
bandits, ordered by their positions in the circle, and the drawn number n. Output the names of
the bandits as they are eliminated and the name of the winner. The obvious choice of data
structure for this problem is a circularly linked list.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
7. A ......................... linked list consists of a number of nodes in which each node has a next
pointer to the following element.
8. To find information in a linked list one must start from the ......................... of the list and
traverse the list sequentially until it finds (or not find) the node.
9. A ......................... linked list is a list that has two references, one to the next node and
another to previous node.
10. The design of the node allows flexibility of storing any ......................... as the linked list
data.
11. A ......................... list is a more general linked list with multiple links from nodes.
102 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY