Page 59 - DCAP201_FUNDAMENTALS_OF_DATA_STRUCTURES
P. 59
Fundamentals of Data Structures
Notes
Did u know? A row is a horizontal list of elements and a column is a vertical list of elements.
In the following figure 4.5, we may observe that two-dimensional array A has 3 rows and
4 columns. Let we emphasize that each row contains those elements with the same first subscript,
and each column contains those elements with the same second subscript.
Figure 4.5: Two-dimensional 3 x 4 array A
Source: http://www.csbdu.in/econtent/DataStructures/Unit1-DS.pdf
Example:
Let we go through this example,
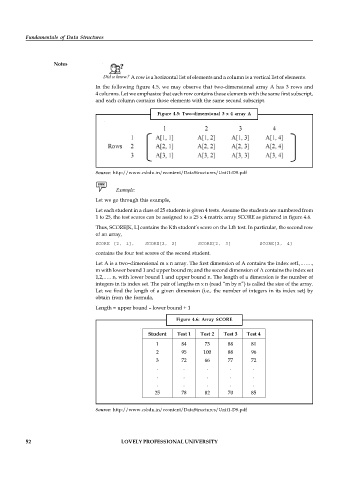
Let each student in a class of 25 students is given 4 tests. Assume the students are numbered from
1 to 25, the test scores can be assigned to a 25 x 4 matrix array SCORE as pictured in figure 4.6.
Thus, SCORE[K, L] contains the Kth student’s score on the Lth test. In particular, the second row
of an array,
SCORE [2, 1], SCORE[2, 2] SCORE[2, 3] SCORE[2, 4]
contains the four test scores of the second student.
Let A is a two–dimensional m x n array. The first dimension of A contains the index set1,…….,
m with lower bound 1 and upper bound m; and the second dimension of A contains the index set
1,2,….. n, with lower bound 1 and upper bound n. The length of a dimension is the number of
integers in its index set. The pair of lengths m x n (read “m by n”) is called the size of the array.
Let we find the length of a given dimension (i.e., the number of integers in its index set) by
obtain from the formula,
Length = upper bound – lower bound + 1
Figure 4.6: Array SCORE
Student Test 1 Test 2 Test 3 Test 4
1 84 73 88 81
2 95 100 88 96
3 72 66 77 72
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
25 78 82 70 85
Source: http://www.csbdu.in/econtent/DataStructures/Unit1-DS.pdf
52 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY