Page 158 - DCAP207_NETWORKS_DCAP406_COMPUTER_NETWORKS
P. 158
Unit 10: Network Layer in the Internet
network, this class is used. It uses the only one octet to define prefix length. The numbers Notes
of network, which can be accommodated, are 2 or 128. However, out of these 128 addresses,
8
2 are used for administrative purposes and thus 126 addresses are available as prefix
length. The remaining 3 octets are used for identifying up to 2 or 16,777,214 host IDs.
24
Class B: It uses 16 bits for both the network address and host address. In this case the first
two bits are always 10. It is reserved for IP unicast addresses. It uses
2 octets for a particular network while remaining two octets for host IDs. They are
particularly used for medium to large-sized networks. The Class B addresses can be
provided to 16,384 networks with up to 65,536 hosts per network.
Class C: It is reserved for IP unicast addresses. They are meant for small networks. The first
3 octets specify a particular network and the last one octet specify host IDs. The Class C
addresses may be used up to 2,097,152 networks with up to 254 hosts per network. Its first
three bits are always set to 110.
Class D: It defines IP multicast addresses.
Class E: These addresses were reserved for experimental uses.
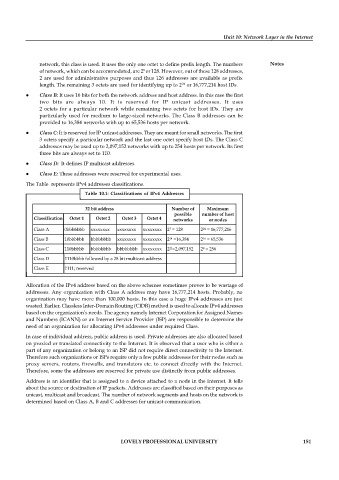
The Table represents IPv4 addresses classifications.
Table 10.1: Classifications of IPv4 Addresses
32 bit address Number of Maximum
possible number of host
Classification Octet 1 Octet 2 Octet 3 Octet 4 networks or nodes
Class A 0bbbbbbb xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx 2 = 128 2 = 16,777,216
7
24
16
14
Class B 10bbbbbb bbbbbbbb xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx 2 =16,384 2 = 65,536
8
Class C 110bbbbb bbbbbbbb bbbbbbbb xxxxxxxx 2 =2,097,152 2 = 256
21
Class D 1110bbbb followed by a 28 bit multicast address
Class E 1111; reserved
Allocation of the IPv4 address based on the above schemes sometimes proves to be wastage of
addresses. Any organization with Class A address may have 16,777,214 hosts. Probably, no
organization may have more than 100,000 hosts. In this case a huge IPv4 addresses are just
wasted. Earlier, Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) method is used to allocate IPv4 addresses
based on the organization’s needs. The agency namely Internet Corporation for Assigned Names
and Numbers (ICANN) or an Internet Service Provider (ISP) are responsible to determine the
need of an organization for allocating IPv4 addresses under required Class.
In case of individual address, public address is used. Private addresses are also allocated based
on proxied or translated connectivity to the Internet. It is observed that a user who is either a
part of any organization or belong to an ISP did not require direct connectivity to the Internet.
Therefore such organizations or ISPs require only a few public addresses for their nodes such as
proxy servers, routers, firewalls, and translators etc. to connect directly with the Internet.
Therefore, some the addresses are reserved for private use distinctly from public addresses.
Address is an identifier that is assigned to a device attached to a node in the Internet. It tells
about the source or destination of IP packets. Addresses are classified based on their purposes as
unicast, multicast and broadcast. The number of network segments and hosts on the network is
determined based on Class A, B and C addresses for unicast communication.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 151