Page 179 - DCAP207_NETWORKS_DCAP406_COMPUTER_NETWORKS
P. 179
Computer Networks/Networks
Notes The TCP Service Model
TCP service model is consisting of sockets, which are used to create end points for TCP service
at the host machines. It specifies the addressing format, the type of service and the protocol. Each
socket possesses a socket number consisting of the IP address of the host and a 16-bit number
local to that host which is referred as a port. Some of the well-known ports are 21 for FTP, 23 for
telnet, 25for SMTP, 79 for finger, 80 for HTTP, etc. TCP provides a connection type service with
full duplex point-to-point connection. That is, a logical connection must be established prior to
communication. The TCP connection is byte stream instead of message stream. The TCP segment
size is determined by the network’s Maximum Transfer Unit (MTU), which is generally consisting
of 1500 bytes. Because of this a continuous transmission of large amount of data is possible. It
ensures a highly reliable data transmission for upper layers using IP protocol. This is possible
because TCP uses positive acknowledgement to confirm the sender about the proper reception
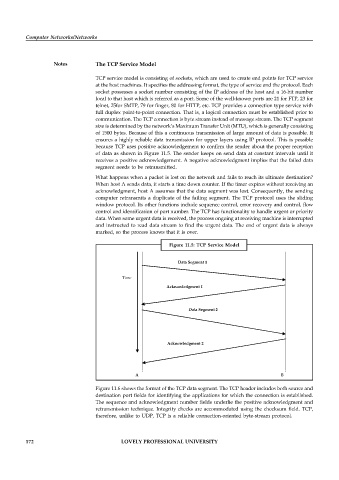
of data as shown in Figure 11.5. The sender keeps on send data at constant intervals until it
receives a positive acknowledgement. A negative acknowledgment implies that the failed data
segment needs to be retransmitted.
What happens when a packet is lost on the network and fails to reach its ultimate destination?
When host A sends data, it starts a time down counter. If the timer expires without receiving an
acknowledgment, host A assumes that the data segment was lost. Consequently, the sending
computer retransmits a duplicate of the failing segment. The TCP protocol uses the sliding
window protocol. Its other functions include sequence control, error recovery and control, flow
control and identification of port number. The TCP has functionality to handle urgent or priority
data. When some urgent data is received, the process ongoing at receiving machine is interrupted
and instructed to read data stream to find the urgent data. The end of urgent data is always
marked, so the process knows that it is over.
Figure 11.5: TCP Service Model
Data Segment 1
Time
Acknowledgment 1
Data Segment 2
Acknowledgment 2
A B
Figure 11.6 shows the format of the TCP data segment. The TCP header includes both source and
destination port fields for identifying the applications for which the connection is established.
The sequence and acknowledgment number fields underlie the positive acknowledgment and
retransmission technique. Integrity checks are accommodated using the checksum field. TCP,
therefore, unlike to UDP, TCP is a reliable connection-oriented byte-stream protocol.
172 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY