Page 36 - DCAP207_NETWORKS_DCAP406_COMPUTER_NETWORKS
P. 36
Unit 3: Physical Layer
3.1 Transmission Concepts and Terms Notes
Before discussing different kinds of transmission medium, it becomes necessary to know a little
about the basic concepts and terminology associated with the transmission of a signal.
Frequency Spectrum:
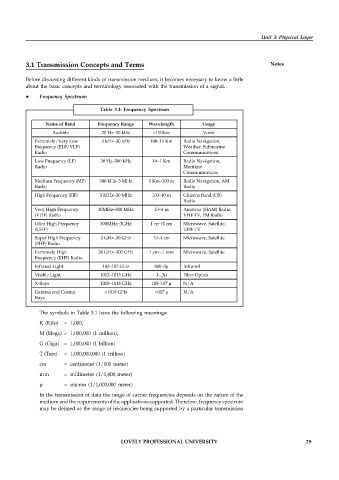
Table 3.1: Frequency Spectrum
Name of Band Frequency Range Wavelength Usage
Audible 20 Hz–20 kHz >100Km Voice
Extremely/Very Low 3 kHz–30 kHz 100–10 Km Radio Navigation,
Frequency (ELF/VLF) Weather, Submarine
Radio Communications
Low Frequency (LF) 30 Hz–300 kHz 10–1 Km Radio Navigation,
Radio Maritime
Communications
Medium Frequency (MF) 300 kHz–3 MHz 1 Km–100 m Radio Navigation, AM
Radio Radio
High Frequency (HF) 3 MHz–30 MHz 100–10 m Citizens Band (CB)
Radio
Very High Frequency 30MHz–300 MHz 10–1 m Amateur (HAM) Radio,
(VHF) Radio VHF TV, FM Radio
Ultra High Frequency 300MHz–3GHz 1 m–10 cm Microwave, Satellite,
(UHF) UHF TV
Super High Frequency 3 GHz–30 GHz 10–1 cm Microwave, Satellite
(SHF) Radio
Extremely High 30 GHz–300 GHz 1 cm–.1 mm Microwave, Satellite
Frequency (EHF) Radio
Infrared Light 103–105 GHz 300–3µ Infrared
Visible Light 1013–1015 GHz 1–.3µ Fiber Optics
X-Rays 1015–1018 GHz 103–107 µ N/A
Gamma and Cosmic >1018 GHz <017 µ N/A
Rays
The symbols in Table 3.1 have the following meanings:
K (Kilo) = 1,000,
M (Mega) = 1,000,000 (1 million),
G (Giga) = 1,000,000 (1 billion)
T (Tera) = 1,000,000,000 (1 trillion)
cm = centimeter (1/100 meter)
mm = millimeter (1/1,000 meter)
µ = micron (1/1,000,000 meter)
In the transmission of data the range of carrier frequencies depends on the nature of the
medium and the requirements of the applications supported. Therefore, frequency spectrum
may be defined as the range of frequencies being supported by a particular transmission
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 29