Page 55 - DCAP207_NETWORKS_DCAP406_COMPUTER_NETWORKS
P. 55
Computer Networks/Networks
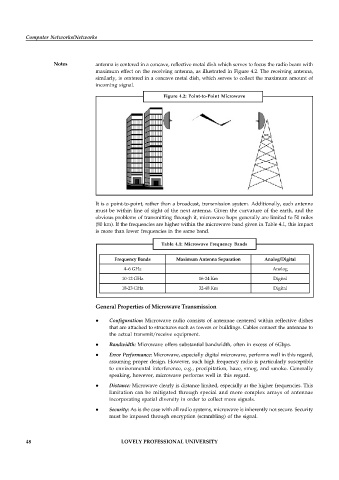
Notes antenna is centered in a concave, reflective metal dish which serves to focus the radio beam with
maximum effect on the receiving antenna, as illustrated in Figure 4.2. The receiving antenna,
similarly, is centered in a concave metal dish, which serves to collect the maximum amount of
incoming signal.
Figure 4.2: Point-to-Point Microwave
It is a point-to-point, rather than a broadcast, transmission system. Additionally, each antenna
must be within line of sight of the next antenna. Given the curvature of the earth, and the
obvious problems of transmitting through it, microwave hops generally are limited to 50 miles
(80 km). If the frequencies are higher within the microwave band given in Table 4.1, this impact
is more than lower frequencies in the same band.
Table 4.1: Microwave Frequency Bands
Frequency Bands Maximum Antenna Separation Analog/Digital
4–6 GHz Analog
10-12 GHz 16-24 Km Digital
18-23 GHz 32-48 Km Digital
General Properties of Microwave Transmission
Configuration: Microwave radio consists of antennae centered within reflective dishes
that are attached to structures such as towers or buildings. Cables connect the antennae to
the actual transmit/receive equipment.
Bandwidth: Microwave offers substantial bandwidth, often in excess of 6Gbps.
Error Performance: Microwave, especially digital microwave, performs well in this regard,
assuming proper design. However, such high frequency radio is particularly susceptible
to environmental interference, e.g., precipitation, haze, smog, and smoke. Generally
speaking, however, microwave performs well in this regard.
Distance: Microwave clearly is distance limited, especially at the higher frequencies. This
limitation can be mitigated through special and more complex arrays of antennae
incorporating spatial diversity in order to collect more signals.
Security: As is the case with all radio systems, microwave is inherently not secure. Security
must be imposed through encryption (scrambling) of the signal.
48 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY