Page 108 - Open Soource Technologies 304.indd
P. 108
Web Technologies-I
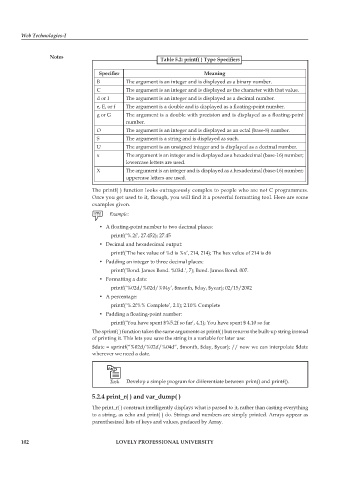
Notes Table 5.2: printf( ) Type Specifiers
Specifier Meaning
B The argument is an integer and is displayed as a binary number.
C The argument is an integer and is displayed as the character with that value.
d or I The argument is an integer and is displayed as a decimal number.
e, E, or f The argument is a double and is displayed as a floating-point number.
g or G The argument is a double with precision and is displayed as a floating-point
number.
O The argument is an integer and is displayed as an octal (base-8) number.
S The argument is a string and is displayed as such.
U The argument is an unsigned integer and is displayed as a decimal number.
x The argument is an integer and is displayed as a hexadecimal (base-16) number;
lowercase letters are used.
X The argument is an integer and is displayed as a hexadecimal (base-16) number;
uppercase letters are used.
The printf( ) function looks outrageously complex to people who are not C programmers.
Once you get used to it, though, you will find it a powerful formatting tool. Here are some
examples given.
• A floating-point number to two decimal places:
printf(‘%.2f’, 27.452); 27.45
• Decimal and hexadecimal output:
printf(‘The hex value of %d is %x’, 214, 214); The hex value of 214 is d6
• Padding an integer to three decimal places:
printf(‘Bond. James Bond. %03d.’, 7); Bond. James Bond. 007.
• Formatting a date:
printf(‘%02d/%02d/%04y’, $month, $day, $year); 02/15/2002
• A percentage:
printf(‘%.2f%% Complete’, 2.1); 2.10% Complete
• Padding a floating-point number:
printf(‘You have spent $%5.2f so far’, 4.1); You have spent $ 4.10 so far
The sprintf( ) function takes the same arguments as printf( ) but returns the built-up string instead
of printing it. This lets you save the string in a variable for later use:
$date = sprintf(“%02d/%02d/%04d”, $month, $day, $year); // now we can interpolate $date
wherever we need a date.
Develop a simple program for differentiate between print() and printf().
5.2.4 print_r( ) and var_dump( )
The print_r( ) construct intelligently displays what is passed to it, rather than casting everything
to a string, as echo and print( ) do. Strings and numbers are simply printed. Arrays appear as
parenthesized lists of keys and values, prefaced by Array.
102 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY