Page 51 - Open Soource Technologies 304.indd
P. 51
Unit 2: Language Basics
Casting Operators Notes
Although PHP is a weakly typed language, there are occasions when it is useful to consider a
value as a specific type. The casting operators, (int), (float), (string), (bool), (array), and (object),
allow you to force a value into a particular type. To use a casting operator, put the operator to
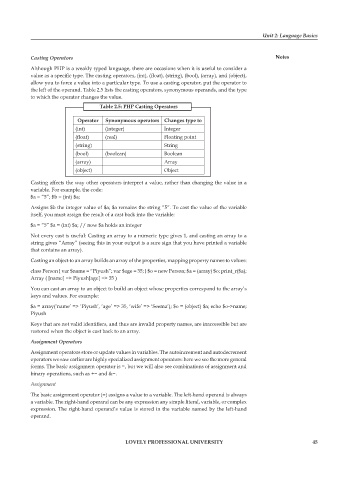
the left of the operand. Table 2.5 lists the casting operators, synonymous operands, and the type
to which the operator changes the value.
Table 2.5: PHP Casting Operators
Operator Synonymous operators Changes type to
(int) (integer) Integer
(float) (real) Floating point
(string) String
(bool) (boolean) Boolean
(array) Array
(object) Object
Casting affects the way other operators interpret a value, rather than changing the value in a
variable. For example, the code:
$a = “5”; $b = (int) $a;
Assigns $b the integer value of $a; $a remains the string “5”. To cast the value of the variable
itself, you must assign the result of a cast back into the variable:
$a = “5” $a = (int) $a; // now $a holds an integer
Not every cast is useful: Casting an array to a numeric type gives 1, and casting an array to a
string gives “Array” (seeing this in your output is a sure sign that you have printed a variable
that contains an array).
Casting an object to an array builds an array of the properties, mapping property names to values:
class Person { var $name = “Piyush”; var $age = 35; } $o = new Person; $a = (array) $o; print_r($a);
Array ( [name] => Piyush[age] => 35 )
You can cast an array to an object to build an object whose properties correspond to the array’s
keys and values. For example:
$a = array(‘name’ => ‘Piyush’, ‘age’ => 35, ‘wife’ => ‘Seema’); $o = (object) $a; echo $o->name;
Piyush
Keys that are not valid identifiers, and thus are invalid property names, are inaccessible but are
restored when the object is cast back to an array.
Assignment Operators
Assignment operators store or update values in variables. The autoincrement and autodecrement
operators we saw earlier are highly specialized assignment operators: here we see the more general
forms. The basic assignment operator is =, but we will also see combinations of assignment and
binary operations, such as += and &=.
Assignment
The basic assignment operator (=) assigns a value to a variable. The left-hand operand is always
a variable. The right-hand operand can be any expression any simple literal, variable, or complex
expression. The right-hand operand’s value is stored in the variable named by the left-hand
operand.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 45