Page 219 - Open Soource Technologies 304.indd
P. 219
Unit 9: Menus and Dialog Boxes
9.7.1 Prompting for Input with InputBox
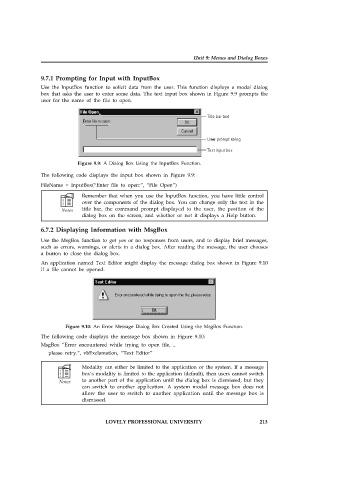
Use the InputBox function to solicit data from the user. This function displays a modal dialog
box that asks the user to enter some data. The text input box shown in Figure 9.9 prompts the
user for the name of the file to open.
Figure 9.9: A Dialog Box Using the InputBox Function.
The following code displays the input box shown in Figure 9.9:
FileName = InputBox(“Enter file to open:”, “File Open”)
Remember that when you use the InputBox function, you have little control
over the components of the dialog box. You can change only the text in the
title bar, the command prompt displayed to the user, the position of the
dialog box on the screen, and whether or not it displays a Help button.
6.7.2 Displaying Information with MsgBox
Use the MsgBox function to get yes or no responses from users, and to display brief messages,
such as errors, warnings, or alerts in a dialog box. After reading the message, the user chooses
a button to close the dialog box.
An application named Text Editor might display the message dialog box shown in Figure 9.10
if a file cannot be opened.
Figure 9.10: An Error Message Dialog Box Created Using the MsgBox Function.
The following code displays the message box shown in Figure 9.10:
MsgBox “Error encountered while trying to open file, _
please retry.”, vbExclamation, “Text Editor”
Modality can either be limited to the application or the system. If a message
box’s modality is limited to the application (default), then users cannot switch
to another part of the application until the dialog box is dismissed, but they
can switch to another application. A system modal message box does not
allow the user to switch to another application until the message box is
dismissed.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 213