Page 47 - Open Soource Technologies 304.indd
P. 47
Unit 3: Understanding Controls and Control Events
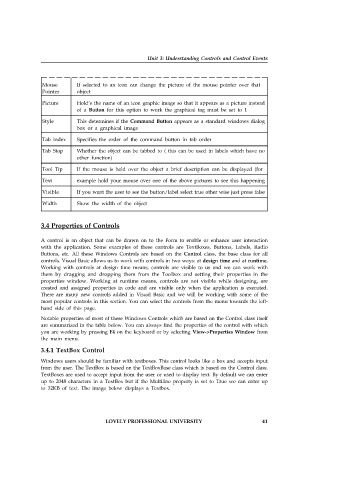
Mouse If selected to an icon can change the picture of the mouse pointer over that
Pointer object
Picture Hold’s the name of an icon graphic image so that it appears as a picture instead
of a Button for this option to work the graphical tag must be set to 1
Style This determines if the Command Button appears as a standard windows dialog
box or a graphical image
Tab index Specifies the order of the command button in tab order
Tab Stop Whether the object can be tabbed to ( this can be used in labels which have no
other function)
Tool Tip If the mouse is held over the object a brief description can be displayed (for
Text example hold your mouse over one of the above pictures to see this happening
Visible If you want the user to see the button/label select true other wise just press false
Width Show the width of the object
3.4 Properties of Controls
A control is an object that can be drawn on to the Form to enable or enhance user interaction
with the application. Some examples of these controls are TextBoxes, Buttons, Labels, Radio
Buttons, etc. All these Windows Controls are based on the Control class, the base class for all
controls. Visual Basic allows us to work with controls in two ways: at design time and at runtime.
Working with controls at design time means, controls are visible to us and we can work with
them by dragging and dropping them from the Toolbox and setting their properties in the
properties window. Working at runtime means, controls are not visible while designing, are
created and assigned properties in code and are visible only when the application is executed.
There are many new controls added in Visual Basic and we will be working with some of the
most popular controls in this section. You can select the controls from the menu towards the left-
hand side of this page.
Notable properties of most of these Windows Controls which are based on the Control class itself
are summarized in the table below. You can always find the properties of the control with which
you are working by pressing F4 on the keyboard or by selecting View->Properties Window from
the main menu.
3.4.1 TextBox Control
Windows users should be familiar with textboxes. This control looks like a box and accepts input
from the user. The TextBox is based on the TextBoxBase class which is based on the Control class.
TextBoxes are used to accept input from the user or used to display text. By default we can enter
up to 2048 characters in a TextBox but if the Multiline property is set to True we can enter up
to 32KB of text. The image below displays a Textbox.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 41