Page 71 - DCAP303_MULTIMEDIA_SYSTEMS
P. 71
Unit 4: Image
DWORD Original vertical resolution (pixels/inch) notes
WORD x value of top left of image
WORD y value of top left of image
WORD x value of lower right of image
WORD y value of lower right of image
DWORD Reserved
This is followed by the image data. Each record of a PICT v2.0 file consists of a two-byte opcode
followed by the actual data.
To avoid the collision opcodes, data must be aligned on 16-byte boundaries
and that certain opcodes in PICT v1.0 and v2.0 files should be interpreted
differently.
4.9 Windows imaging file format (WiM)
This topic introduces the Microsoft Windows Imaging (WIM) file format. The WIM is a file-based
disk image format that was introduced in Windows Vista. WIM files are compressed packages that
contain a number of related files. The format of a WIM file is optimized for maximum compression
with LZX, for fast compression with XPRESS, or uncompressed.
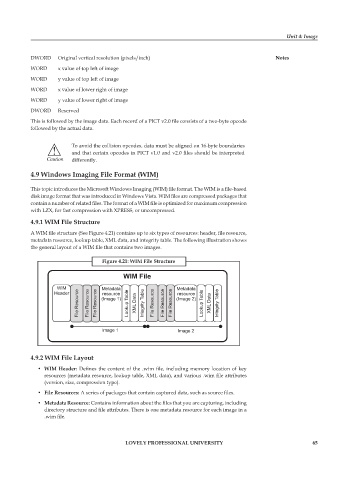
4.9.1 WiM file structure
A WIM file structure (See Figure 4.21) contains up to six types of resources: header, file resource,
metadata resource, lookup table, XML data, and integrity table. The following illustration shows
the general layout of a WIM file that contains two images.
figure 4.21: WiM file structure
4.9.2 WiM file Layout
• WiM Header: Defines the content of the .wim file, including memory location of key
resources (metadata resource, lookup table, XML data), and various .wim file attributes
(version, size, compression type).
• file resources: A series of packages that contain captured data, such as source files.
• Metadata resource: Contains information about the files that you are capturing, including
directory structure and file attributes. There is one metadata resource for each image in a
.wim file.
LoveLy professionaL University 65