Page 77 - DCAP305_PRINCIPLES_OF_SOFTWARE_ENGINEERING
P. 77
Unit 4: Introduction to Validation, Metrics
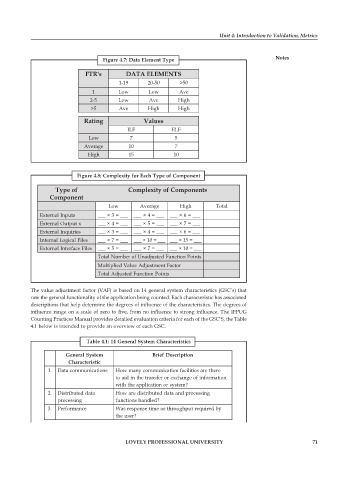
Figure 4.7: Data Element Type Notes
FTR's DATA ELEMENTS
1-19 20-50 >50
1 Low Low Ave
2-5 Low Ave High
>5 Ave High High
Rating Values
ILF ELF
Low 7 5
Average 10 7
High 15 10
Figure 4.8: Complexity for Each Type of Component
Type of Complexity of Components
Component
Low Average High Total
External Inputs ___ × 3 = ___ ___ × 4 = ___ ___ × 6 = ___
External Output x ___ × 4 = ___ ___ × 5 = ___ ___ × 7 = ___
External Inquiries ___ × 3 = ___ ___ × 4 = ___ ___ × 6 = ___
Internal Logical Files ___ × 7 = ___ ___ × 10 = ___ ___ × 15 = ___
External Interface Files ___ × 5 = ___ ___ × 7 = ___ ___ × 10 = ___
Total Number of Unadjusted Function Points
Multiplied Value Adjustment Factor
Total Adjusted Function Points
The value adjustment factor (VAF) is based on 14 general system characteristics (GSC’s) that
rate the general functionality of the application being counted. Each characteristic has associated
descriptions that help determine the degrees of influence of the characteristics. The degrees of
influence range on a scale of zero to five, from no influence to strong influence. The IFPUG
Counting Practices Manual provides detailed evaluation criteria for each of the GSC’S, the Table
4.1 below is intended to provide an overview of each GSC.
Table 4.1: 14 General System Characteristics
General System Brief Description
Characteristic
1. Data communications How many communication facilities are there
to aid in the transfer or exchange of information
with the application or system?
2. Distributed data How are distributed data and processing
processing functions handled?
3. Performance Was response time or throughput required by
the user?
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 71