Page 183 - DCAP312_WEB_TECHNOLOGIES_II
P. 183
Unit 9: The Database Model
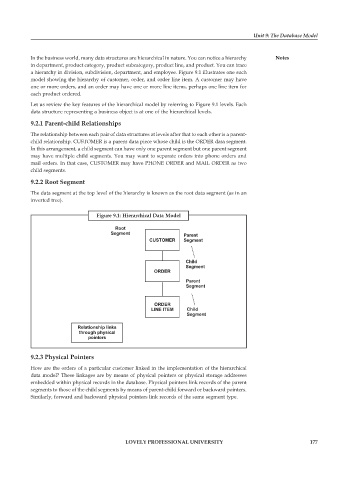
In the business world, many data structures are hierarchical in nature. You can notice a hierarchy Notes
in department, product category, product subcategory, product line, and product. You can trace
a hierarchy in division, subdivision, department, and employee. Figure 9.1 illustrates one such
model showing the hierarchy of customer, order, and order line item. A customer may have
one or more orders, and an order may have one or more line items, perhaps one line item for
each product ordered.
Let us review the key features of the hierarchical model by referring to Figure 9.1 levels. Each
data structure representing a business object is at one of the hierarchical levels.
9.2.1 Parent-child Relationships
The relationship between each pair of data structures at levels after that to each other is a parent-
child relationship. CUSTOMER is a parent data piece whose child is the ORDER data segment.
In this arrangement, a child segment can have only one parent segment but one parent segment
may have multiple child segments. You may want to separate orders into phone orders and
mail orders. In that case, CUSTOMER may have PHONE ORDER and MAIL ORDER as two
child segments.
9.2.2 Root Segment
The data segment at the top level of the hierarchy is known as the root data segment (as in an
inverted tree).
Figure 9.1: Hierarchical Data Model
9.2.3 Physical Pointers
How are the orders of a particular customer linked in the implementation of the hierarchical
data model? These linkages are by means of physical pointers or physical storage addresses
embedded within physical records in the database. Physical pointers link records of the parent
segments to those of the child segments by means of parent-child forward or backward pointers.
Similarly, forward and backward physical pointers link records of the same segment type.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 177