Page 188 - DCAP304_DCAP515_SOFTWARE_PROJECT_MANAGEMENT
P. 188
Software Project Management
Notes 3. The risk analysis includes the magnitude of consequences and the chance that these
consequences may come to life.
4. In the evaluation of risks the consequences are leveled (ranked) after their magnitude, so
if needed the right treatment will be applied.
5. If the risk is low or has a low-priority it can be taken care of (by routine knowledge) or be
accepted at this stage. But if it is a high-priority risk, a plan for managing is instantly laid
out. According to AS/NZS 4360 the following plan should be used:
Identify treatment options
Evaluate treatment options
Select treatment options
Prepare treatment plan
Implement plans
6. Monitoring and reviewing are used to overlook the risk management cycle and track
changes within it so new contexts (continues improvements) can be made and the final
treatment of the risks improves.
7. Communication and consultation at every new step in the process is very important to
people on the inside of the company as for people on the outside (stakeholders, investors).
Did u know? What is AS/NZS 4360?
AS/NZS 4360 is a generic guide for risk management so that it applies to all forms of
organizations. Risk management” is defined as ‘the culture, processes and structures that
are directed towards realizing potential opportunities whilst managing adverse effects.’
The model of the risk management process AS/NZS 4360 consists of three major elements.
The risk management workflow, monitor and review, and finally communication and
consult.
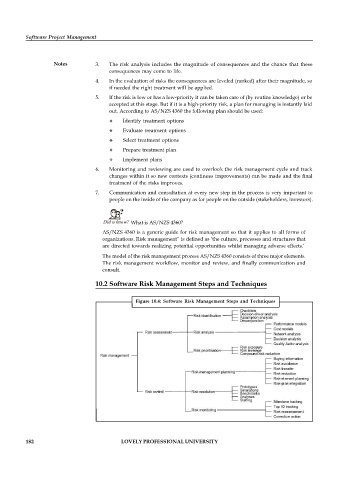
10.2 Software Risk Management Steps and Techniques
Figure 10.4: Software Risk Management Steps and Techniques
182 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY