Page 128 - DMGT409Basic Financial Management
P. 128
Unit 7: Capital Budgeting
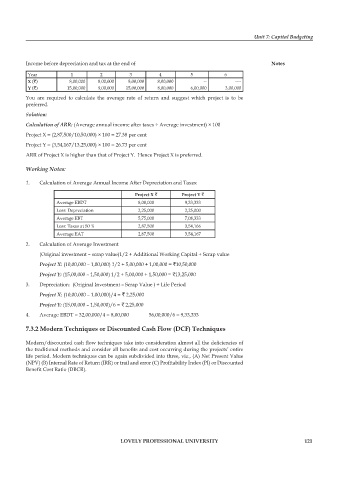
Income before depreciation and tax at the end of Notes
Year 1 2 3 4 5 6
X (`) 8,00,000 8,00,000 8,00,000 8,00,000 -- ----
Y (`) 15,00,000 9,00,000 15,00,000 8,00,000 6,00,000 3,00,000
You are required to calculate the average rate of return and suggest which project is to be
preferred.
Solution:
Calculation of ARR: (Average annual income after taxes ÷ Average investment) × 100
Project X = (2,87,500/10,50,000) × 100 = 27.38 per cent
Project Y = (3,54,167/13,25,000) × 100 = 26.73 per cent
ARR of Project X is higher than that of Project Y. Hence Project X is preferred.
Working Notes:
1. Calculation of Average Annual Income After Depreciation and Taxes:
Project X ` Project Y `
Average EBDT 8,00,000 9,33,333
Less: Depreciation 2,25,000 2,25,000
Average EBT 5,75,000 7,08,333
Less: Taxes at 50 % 2,87,500 3,54,166
Average EAT 2,87,500 3,54,167
2. Calculation of Average Investment
(Original investment – scrap value)1/2 + Additional Working Capital + Scrap value
Project X: (10,00,000 – 1,00,000) 1/2 + 5,00,000 + 1,00,000 = `10,50,000
Project Y: (15,00,000 – 1,50,000) 1/2 + 5,00,000 + 1,50,000 = `13,25,000
3. Depreciation: (Original Investment – Scrap Value ) ÷ Life Period
Project X: (10,00,000 – 1,00,000)/4 = ` 2,25,000
Project Y: (15,00,000 – 1,50,000)/6 = ` 2,25,000
4. Average EBDT = 32,00,000/4 = 8,00,000 56,00,000/6 = 9,33,333
7.3.2 Modern Techniques or Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Techniques
Modern/discounted cash flow techniques take into consideration almost all the defi ciencies of
the traditional methods and consider all benefits and cost occurring during the projects’ entire
life period. Modern techniques can be again subdivided into three, viz., (A) Net Present Value
(NPV) (B) Internal Rate of Return (IRR) or trail and error (C) Profitability Index (PI) or Discounted
Benefit Cost Ratio (DBCR).
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 121