Page 261 - DCAP404 _Object Oriented Programming
P. 261
Object-oriented Programming
Notes
Example: The following program reads an integer and prints the input on the console.
#include <iostream> // Header for stream I/O.
int main(void)
{
int p; // variable to hold the input integer
cout << “Enter an integer: “;
cin >> p;
cout << “\n You have entered “ << p;
}
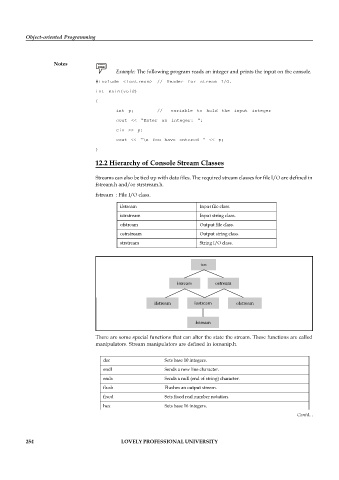
12.2 Hierarchy of Console Stream Classes
Streams can also be tied up with data files. The required stream classes for file I/O are defined in
fstream.h and/or strstream.h.
fstream : File I/O class.
ifstream Input file class.
istrstream Input string class.
ofstream Output file class.
ostrstream Output string class.
strstream String I/O class.
ios
istream ostream
ifstream iostream ofstream
fstream
There are some special functions that can alter the state the stream. These functions are called
manipulators. Stream manipulators are defined in iomanip.h.
dec Sets base 10 integers.
endl Sends a new line character.
ends Sends a null (end of string) character.
flush Flushes an output stream.
fixed Sets fixed real number notation.
hex Sets base 16 integers.
oct Sets base 8 integers. Contd...
ws Discard white space on input.
setbase(int) Sets integer conversion base (0, 8, 10 or 16 where 0 sets base 10).
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY
254 setfill(int) Sets fill character.
setprecision(int) Sets precision.
setw(int) Sets field width.
resetiosflags(long) Clears format state as specified by argument.
setiosflags(long) Sets format state as specified by argument.