Page 35 - DCAP404 _Object Oriented Programming
P. 35
Object-oriented Programming
Notes
Notes The operators, ‘++’ and ‘—’ , are best used in simple expressions like the ones shown
above.
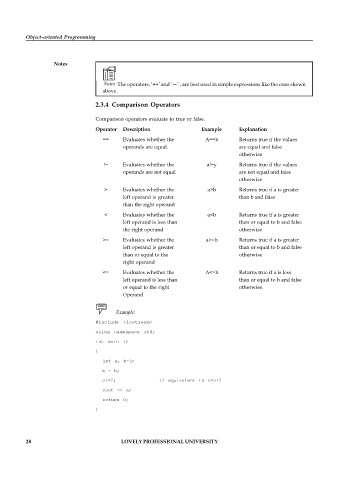
2.3.4 Comparison Operators
Comparison operators evaluate to true or false.
Operator Description Example Explanation
== Evaluates whether the A==b Returns true if the values
operands are equal. are equal and false
otherwise
!= Evaluates whether the a!=y Returns true if the values
operands are not equal are not equal and false
otherwise
> Evaluates whether the a>b Returns true if a is greater
left operand is greater than b and false
than the right operand
< Evaluates whether the a<b Returns true if a is greater
left operand is less than than or equal to b and false
the right operand otherwise
>= Evaluates whether the a>=b Returns true if a is greater
left operand is greater than or equal to b and false
than or equal to the otherwise
right operand
<= Evaluates whether the A<=b Returns true if a is less
left operand is less than than or equal to b and false
or equal to the right otherwise.
Operand
Example:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int a, b=3;
a = b;
a+=2; // equivalent to a=a+2
cout << a;
return 0;
}
28 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY