Page 181 - DCAP406_DCAP_207_Computer Networks
P. 181
Computer Networks/Networks
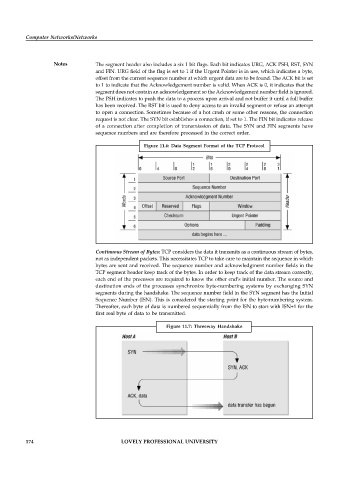
Notes The segment header also includes a six 1 bit flags. Each bit indicates URG, ACK PSH, RST, SYN
and FIN. URG field of the flag is set to 1 if the Urgent Pointer is in use, which indicates a byte,
offset from the current sequence number at which urgent data are to be found. The ACK bit is set
to 1 to indicate that the Acknowledgement number is valid. When ACK is 0, it indicates that the
segment does not contain an acknowledgement so the Acknowledgement number field is ignored.
The PSH indicates to push the data to a process upon arrival and not buffer it until a full buffer
has been received. The RST bit is used to deny access to an invalid segment or refuse an attempt
to open a connection. Sometimes because of a hot crash or some other reasons, the connection
request is not clear. The SYN bit establishes a connection, if set to 1. The FIN bit indicates release
of a connection after completion of transmission of data. The SYN and FIN segments have
sequence numbers and are therefore processed in the correct order.
Figure 11.6: Data Segment Format of the TCP Protocol
Continuous Stream of Bytes: TCP considers the data it transmits as a continuous stream of bytes,
not as independent packets. This necessitates TCP to take care to maintain the sequence in which
bytes are sent and received. The sequence number and acknowledgment number fields in the
TCP segment header keep track of the bytes. In order to keep track of the data stream correctly,
each end of the processes are required to know the other end’s initial number. The source and
destination ends of the processes synchronize byte-numbering systems by exchanging SYN
segments during the handshake. The sequence number field in the SYN segment has the Initial
Sequence Number (ISN). This is considered the starting point for the byte-numbering system.
Thereafter, each byte of data is numbered sequentially from the ISN to start with ISN+1 for the
first real byte of data to be transmitted.
Figure 11.7: Threeway Handshake
174 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY