Page 244 - DCAP405_SOFTWARE_ENGINEERING
P. 244
Unit 14: Data Modeling
Notes
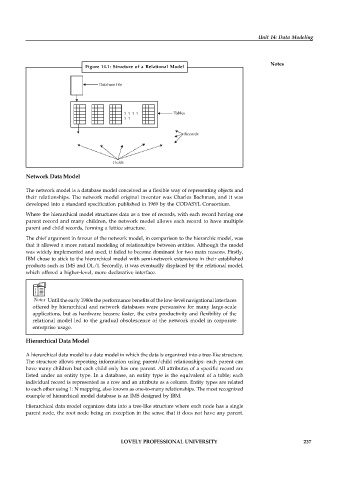
Figure 14.1: Structure of a Relational Model
Database file
? ? ? ? Tables
? ?
Records
Fields
Network Data Model
The network model is a database model conceived as a flexible way of representing objects and
their relationships. The network model original inventor was Charles Bachman, and it was
developed into a standard specification published in 1969 by the CODASYL Consortium.
Where the hierarchical model structures data as a tree of records, with each record having one
parent record and many children, the network model allows each record to have multiple
parent and child records, forming a lattice structure.
The chief argument in favour of the network model, in comparison to the hierarchic model, was
that it allowed a more natural modeling of relationships between entities. Although the model
was widely implemented and used, it failed to become dominant for two main reasons. Firstly,
IBM chose to stick to the hierarchical model with semi-network extensions in their established
products such as IMS and DL/I. Secondly, it was eventually displaced by the relational model,
which offered a higher-level, more declarative interface.
Notes Until the early 1980s the performance benefits of the low-level navigational interfaces
offered by hierarchical and network databases were persuasive for many large-scale
applications, but as hardware became faster, the extra productivity and flexibility of the
relational model led to the gradual obsolescence of the network model in corporate
enterprise usage.
Hierarchical Data Model
A hierarchical data model is a data model in which the data is organized into a tree-like structure.
The structure allows repeating information using parent/child relationships: each parent can
have many children but each child only has one parent. All attributes of a specific record are
listed under an entity type. In a database, an entity type is the equivalent of a table; each
individual record is represented as a row and an attribute as a column. Entity types are related
to each other using 1: N mapping, also known as one-to-many relationships. The most recognized
example of hierarchical model database is an IMS designed by IBM.
Hierarchical data model organizes data into a tree-like structure where each node has a single
parent node, the root node being an exception in the sense that it does not have any parent.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 237