Page 104 - DCAP407_DATA_STRUCTURE
P. 104
Unit 6: Linked List Operations
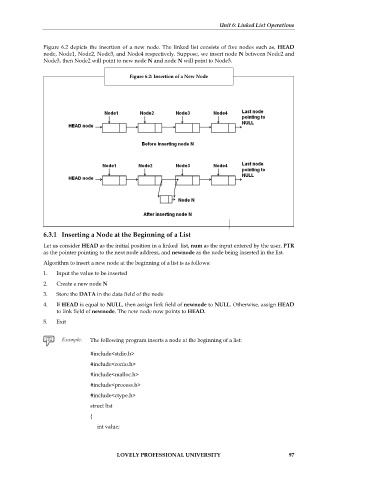
Figure 6.2 depicts the insertion of a new node. The linked list consists of five nodes such as, HEAD
node, Node1, Node2, Node3, and Node4 respectively. Suppose, we insert node N between Node2 and
Node3, then Node2 will point to new node N and node N will point to Node3.
Figure 6.2: Insertion of a New Node
6.3.1 Inserting a Node at the Beginning of a List
Let us consider HEAD as the initial position in a linked list, num as the input entered by the user, PTR
as the pointer pointing to the next node address, and newnode as the node being inserted in the list.
Algorithm to insert a new node at the beginning of a list is as follows:
1. Input the value to be inserted
2. Create a new node N
3. Store the DATA in the data field of the node
4. If HEAD is equal to NULL, then assign link field of newnode to NULL. Otherwise, assign HEAD
to link field of newnode. The new node now points to HEAD.
5. Exit
The following program inserts a node at the beginning of a list:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<process.h>
#include<ctype.h>
struct list
{
int value;
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 97