Page 20 - DCAP407_DATA_STRUCTURE
P. 20
Unit 1: Introduction to Data Structures
Did you know? Each value or key in a tree occurs only once, i.e., there are no duplicates.
Graphs
A graph is also a non-linear data structure. In a tree data structure, all data elements are stored in
definite hierarchical structure. In other words, each node has only one parent node. While in graphs,
each data element is called a vertex and is connected to many other vertexes through connections called
edges.
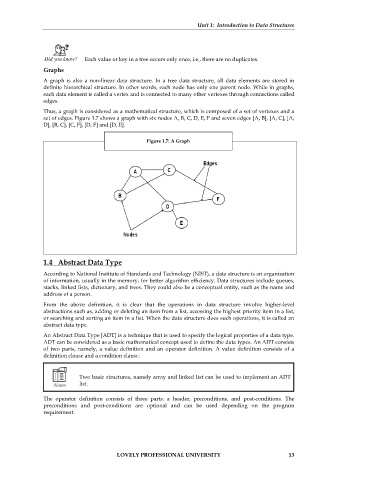
Thus, a graph is considered as a mathematical structure, which is composed of a set of vertexes and a
set of edges. Figure 1.7 shows a graph with six nodes A, B, C, D, E, F and seven edges [A, B], [A, C], [A,
D], [B, C], [C, F], [D, F] and [D, E].
Figure 1.7: A Graph
1.4 Abstract Data Type
According to National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), a data structure is an organization
of information, usually in the memory, for better algorithm efficiency. Data structures include queues,
stacks, linked lists, dictionary, and trees. They could also be a conceptual entity, such as the name and
address of a person.
From the above definition, it is clear that the operations in data structure involve higher-level
abstractions such as, adding or deleting an item from a list, accessing the highest priority item in a list,
or searching and sorting an item in a list. When the data structure does such operations, it is called an
abstract data type.
An Abstract Data Type [ADT] is a technique that is used to specify the logical properties of a data type.
ADT can be considered as a basic mathematical concept used to define the data types. An ADT consists
of two parts, namely, a value definition and an operator definition. A value definition consists of a
definition clause and a condition clause.
Two basic structures, namely array and linked list can be used to implement an ADT
list.
The operator definition consists of three parts: a header, preconditions, and post-conditions. The
preconditions and post-conditions are optional and can be used depending on the program
requirement.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 13